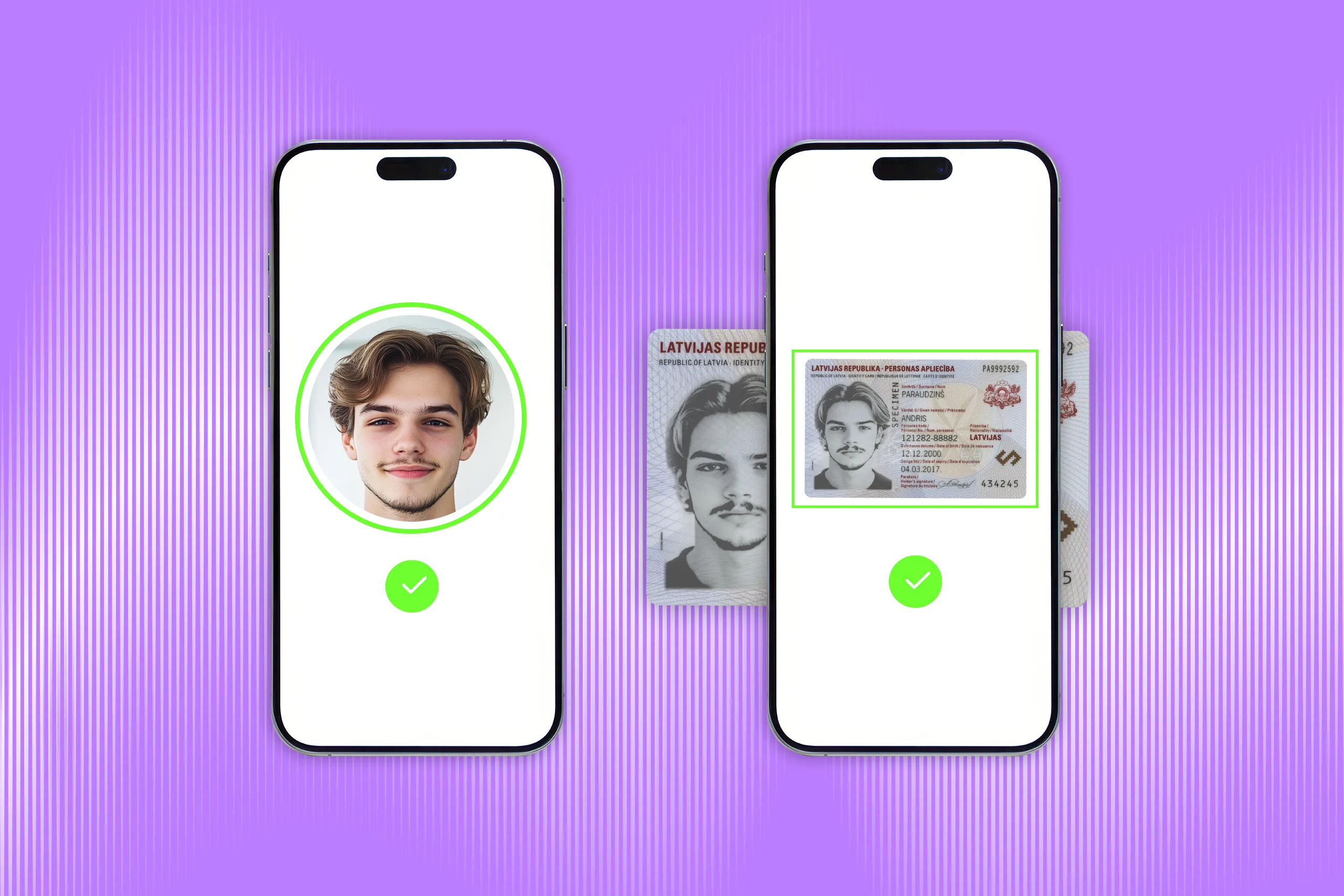
Video identity verification is a proven method for businesses worldwide to confirm customers’ identities remotely. It seems simple to implement and use, but is it still as foolproof as before?
In 2024, 48% of Financial Services companies faced video deepfakes, raising concerns about the reliability and fraud resistance of video identification.
Is the rise of powerful AI-driven identity fraud the only challenge for organizations using video verification for client onboarding and identity confirmation? Is it always effective and suitable for all industries?
This guide provides answers to these questions.
What is video identification? A step-by-step breakdown
Video identification is a process that verifies a user’s identity remotely. It typically involves a live video session with a human inspector, though it can also be fully automated and self-serviced.
Initially adopted by Banking and Fintech companies to meet Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements for remote onboarding and confirming digital transactions, video identification has since expanded into other industries:
Telecoms use it to verify users during SIM card registration.
Healthcare leverages it for telemedicine patient verification and secure medical record access.
E-Government services apply it to identity verification and remote notarization.
Gig economy and ecommerce platforms rely on it to build trust between users and prevent fraud.
Generally, the procedure includes the following steps:

1. ID submission
First, a user must present a government-issued photo ID, such as a passport, driver’s license, or national ID card. This step can take place separately before the video session with an inspector, or be integrated into the live conversation.
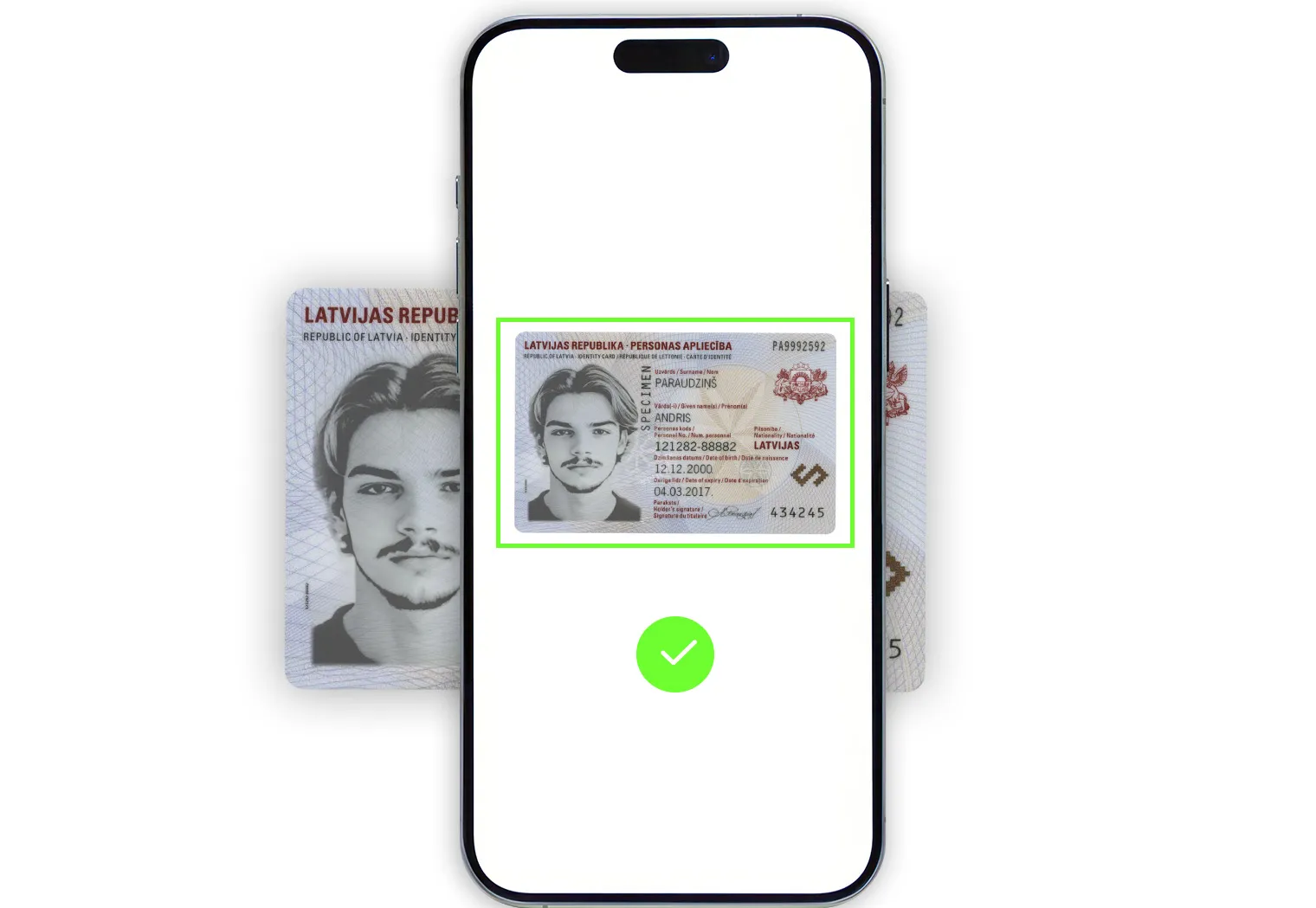

ID verification is often a prerequisite for video identification.
At this stage, the user’s personal details—name, address, date of birth, etc.—can also be collected. The user is often required to fill out the form manually. However, identity verification (IDV) solutions like Regula Document Reader SDK enable automated data extraction during ID scanning, reducing manual entry errors.
Companies usually specify which IDs are eligible for verification. For example, Revolut, a British multinational neobank and Fintech company, requires specific types of ID depending on the country of operation. A universal rule is that the document must not be handwritten, expired, damaged, or unreadable, and the personal information on it must match the data in the user’s Revolut account.
2. Live video session
Next, the session takes place, often assisted by a human agent. However, some companies use a hybrid approach, where the user’s guided interaction is recorded and later reviewed by inspectors.

A live video interaction with a company’s inspector is a core part of customer video identification.
In operator-assisted calls, the agent first explains the process and obtains the user’s consent to verify and process their personal data. The applicant then answers a short questionnaire while the operator requests and scans documents in real time. Alternatively, documents can be uploaded separately.
Additional security checks, such as one-time code verification, may also be performed during the session to confirm the applicant’s phone number.
For example, ICICI Bank (India) offers a video KYC procedure for first-time customers applying for a loan, bank account, or credit card. During the session, a bank officer verifies the applicant’s identity, documents, and signature via a live video call. Before the call, customers must complete preliminary forms, and in some cases, device location detection is required.

Location identification can be part of user verification—an approach used by ICICI Bank.
3. Liveness check
Liveness detection is a critical part of the verification process. In a live session, the agent captures the user’s selfie and compares it against the portrait in the ID and/or a database of registered customers. In an automated process, the user is prompted to perform specific actions, such as nodding or smiling, to confirm they are real and not a deepfake simulation or pre-recorded video.
Once the liveness check is successfully completed, the session (if conducted with an agent) is concluded, and the operator or software submits the data for validation.
4. Data validation
Video identification is finalized during the validation stage, where results are reviewed—either manually or by dedicated software. This process can take anywhere from a few minutes to several days, depending on the purpose of identification.
For example, the operator involved in the video call may conduct validation, review the submitted data, and assign the session a final status: approved or declined. In some cases, additional cross-checks are conducted as part of enhanced due diligence to determine whether the applicant appears on blacklists or is linked to money laundering or other illegal activities.
When video identification is unsuccessful
Video identification is typically considered invalid if inconsistencies or manipulations are detected in the ID document or if there is no match between the document holder and the individual being verified. Additionally, poor internet connection or data transmission issues can cause the process to fail.
Common reasons for unsuccessful identity verification include:
The submitted ID is unsupported, outdated, or invalid (e.g., scans, photocopies, watermarked documents, or blurry/cropped images are presented).
The submitted data doesn’t match the ID, live interview responses, or other verification sources.
The session is interrupted before completion.
The user refuses to follow the operator’s instructions.
The user receives unauthorized assistance from a third party without the operator’s permission.
Suspicious activity is detected, such as suspected money laundering or terrorist financing.
Any of these issues result in onboarding or transaction rejection.
Subscribe to receive a bi-weekly blog digest from Regula
Who governs video identification?
Since video identification includes selfie ID verification, it’s regulated by global, regional, and country-specific standards that ensure compliance with data privacy laws, such as eIDAS 2.0 and the GDPR in the EU. These regulations not only protect users' sensitive personal data but also help prevent fraud, money laundering, and terrorism financing. As a result, anti-money laundering directives like AMLD6 also play a role in governing video identification procedures.
To be effective, compliance measures must strike a balance between security and user privacy—ensuring that fraudsters and criminals are stopped while keeping the process safe, transparent, and seamless for legitimate users.
The list of key regulators by country include:
Estonia: Finantsinspektsioon
Latvia: Financial and Capital Markets Commission
Lithuania: Financial Crime Investigation Service under the Ministry of Interior
Luxembourg: Commission de Surveillance du Secteur Financier
Switzerland: Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority
India: Reserve Bank of India
México: Comisión Nacional de Bienes y Valores
Local regulations often define specific process steps and technical requirements for video identification. For instance, in Spain, SEPBLAC mandates that the submitted ID must include a photo or snapshot of both the front and back of the identification document. In Portugal, Banco de Portugal recommends additional security measures, such as presenting extra identification documents and using facial recognition systems during the process.
Importantly, video identification isn’t universally permitted. Some regions restrict or don’t fully regulate the procedure, making it available only in select countries.
When video identification falls short
Video identification is a widely used method for remote identity verification, but it comes with challenges that businesses of all sizes must consider before relying on it.
To ensure efficient and secure verification, organizations need to address the following issues:
Time-consuming and costly process
Video identification can be handled in-house by human agents or outsourced to third-party providers. Either way, it requires trained personnel, making it a resource-intensive and costly process.
Even with automation, managing high verification volumes can strain resources, leading to delays and increased operational costs—a challenge that particularly affects small- and middle-sized businesses.
User experience issues
While companies claim that live video verification takes just a few minutes, the process can still be stressful and inconvenient for users.
Scheduling an appointment may be required, forcing users to set aside time in their calendar.
Users must ensure a stable internet connection, a working camera, an appropriate environment, and even a presentable appearance for the session.
Technical issues or long wait times can lead to frustration and higher abandonment rates during onboarding.
Security concerns
This issue has two sides.
On one hand, customers expect a highly secure process since biometric data—such as selfies, voice recordings, and personal details—is collected during video identification. For this reason, obtaining user consent is a critical step in live sessions with a human inspector.

Users often worry about how companies handle their video verifications. Public platforms like Reddit have dozens of similar concerns. Source: Reddit.
On the other hand, video identification poses security risks for companies as well. The process is technically vulnerable, especially when third-party platforms like Zoom are used for video calls. In this “uncontrolled environment,” fraudsters can exploit deepfake technology and video injection attacks to bypass verification.
To protect customer privacy and prevent sophisticated presentation attacks, companies must invest in secure infrastructure and advanced fraud detection measures for video identification.
Scalability problems
Human-dependent processes are always difficult to scale, especially as businesses expand into new markets and handle growing customer volumes. A high demand for live video verifications can overwhelm teams, slow down onboarding, and make the process unsustainable.
Additionally, video identification is not widely available in all regions. Countries with limited regulatory frameworks may restrict its use, making geographic expansion challenging for businesses relying on this method.
Inclusivity challenges
Finally, video verification can be inaccessible for certain users. Not everyone has a high-quality camera, a stable internet connection, or the ability to complete video identification due to disabilities.
Relying solely on video-based methods can exclude entire demographics, limiting a company’s customer base and accessibility efforts.
How to get the most out of video identification
While it’s a legal requirement in some industries, video identification also serves as a reliable method to ensure that only genuine users—not fraudsters—gain access to your systems.
However, the process can be improved to enhance user experience, efficiency, and compliance.
Detailed user guidelines
One of the simplest yet most effective ways to improve video identification is by offering clear, step-by-step instructions. Enhancing text-based guidelines with screenshots and short videos helps users understand the process and reduces anxiety about what to expect.
For example, Binance, a cryptocurrency platform, provides a detailed article explaining the purposes of identity verification, outlining each step, and specifying the estimated completion time (up to 15 minutes). They also inform users that video identification may not be available in certain countries, setting clear expectations.

A step-by-step guide, like Binance’s, helps users understand what to expect from the verification process. Source: Binance
Risk-based approach to video identification
Many companies implement a risk-based KYC framework, categorizing customers by their risk level. In this approach, video identification serves as an additional layer of verification for specific high-risk cases.
For example, video identification may be required when onboarding a customer linked to a politically exposed person, or when verifying high-risk transactions, such as large fund withdrawals or international money transfers.
This targeted approach allows companies to focus on suspicious transactions, reducing verification delays for ordinary customers while cutting operational costs.
This is exactly how Kraken, a Crypto platform, operates—using video verification only when necessary to confirm they are communicating with the legitimate account owner. In such cases, customers receive an email requesting a Zoom call.

Kraken uses video identification only for specific cases while providing users with detailed instructions and a test meeting option.
Adding more security layers to the process
Video identification can be combined—or even replaced by—other identity verification methods for greater security and efficiency. These include:
NFC verification (leveraging biometric IDs with e-chips)
Biometric verification (with liveness detection)
For example, UBS, the world’s largest private bank, relies solely on e-passport verification for first-time customers instead of real-time video interviews. This automated enrollment allows the bank to be available for new clients 24/7, reducing verification time to just a few minutes with minimal effort from the customer.
Verification alternatives
Offering multiple verification methods is a practical approach for many companies. These alternatives serve as backups in cases where internet connectivity issues arise or when a customer can’t complete video verification due to personal reasons, such as health conditions. They can also be equivalent options from the start, allowing users to choose the most convenient method.
For example, to verify their identity for GOV.UK One Login, individuals can choose from three verification options to access government services: in-app verification, answering security questions online, and in-person verification at a post office.
Choose Regula as your identity verification ally
Video identification is a powerful tool for verifying customers’ identities in today’s digital landscape. However, to implement it effectively, companies must carefully consider potential risks and challenges. The key is to first define your primary goals—whether it's compliance, security, or fraud prevention—to determine the best verification approach.
Regula is here to support you. In addition to providing reliable SDKs for ID document and biometric verification, we offer expert consultation to help you select and implement the best-fit solution for your needs.
Let’s build a secure verification system together. Schedule a call with our team today.