Modifications in handwritten documents are a common method for fraudulently altering text in letters, paper checks, wills, bills of sale, employment verification letters, and other official documents with handwritten sections.
In order to discover such discrepancies, forensic experts frequently employ non-destructive examination methods. As the capabilities of examination devices continually evolve, these methods become more powerful and accurate. For instance, it’s possible to detect an additional zero written on a check, even when the ink is almost identical in color.
In this blog post, we will introduce three tech-powered ways for detecting alterations, utilizing advanced lighting and filtering techniques.
Let’s zoom in.
Types of fraudulent alterations in documents
Before we dig into the tech details, let’s define some terms.
An “alteration” may be defined as any change to a document that significantly alters its original content. If the text is altered without the consent of the relevant party or individual, such an alteration may be considered fraudulent.
Forensic experts encounter various types of alterations when examining handwritten documents. Some common ones include:
Addition—The insertion of a word, digit, etc., that changes the document’s meaning or value. Typically, additions are placed in blank spaces between lines, in the middle, or at the bottom of the document.
Interlineations—Writing between the lines of a pre-existing document to make corrections. While this is considered a legitimate form of alteration, it can be exploited for illegal purposes.
Overwriting—Writing over an existing entry to improve its legibility or fix spelling mistakes. Fraudsters may use overwriting to change the meaning of the text.
Alterations can be made after a document has been modified by physical, chemical, or mechanical means. These modifications, distinguished by their attributes, are a topic for another article.
Get posts like this in your inbox with the bi-weekly Regula Blog Digest!
Handwritten document examination: Key stages
Forensic handwritten document examination involves scientific analysis to determine whether the original content has been altered.
When dealing with alterations, numerous details should be taken into consideration, including letter form and size, pressure, fluency, slope, stroke sequence, and the type and color of ink used. Importantly, the examination process is always tailored to the specific case and the document in question.
Generally, there are five steps to be followed:

During questioned document examination, forensic experts first evaluate the complete picture, delving into the details step by step:
Content: At this stage, it’s critical to take a close look at specific details in the questioned document, such as names, dates, and numbers, and check for any discrepancies.
Handwriting features: Then, forensic handwriting analysis is performed to identify inconsistencies between the original and questioned lines, such as style, legibility, size, proportion of letters, spacing, and pressure.
Detailed examination of strokes: After that, the expert observes both sides of the questioned document under magnification to detect any aberrations in stroke pressure and fluency. During this stroke attribute analysis, the expert can determine whether everything was written sequentially, with the same instrument, and at the same time. These findings form the basis of their final conclusion.
Assessing ink properties: This step requires special devices to examine the ink characteristics, including type and color, under different light sources (ultraviolet, infrared, narrowband, etc.).
Destructive methods: Finally, if no determination can be made based on the evidence, the experts conducting the examination can agree to use destructive methods.
Note: Destructive examination methods, such as thin-layer chromatography or chemical ink analysis, may be complicated to apply when dealing with alterations in handwritten documents. The examination area is often too small, and can be irreparably damaged during the test. Moreover, this type of method may yield no results. That is also one of the reasons why non-destructive tests are given priority.
What else to consider while inspecting a handwritten document
There are many other factors that examiners should also focus on during forensic handwritten document analysis.
The common list includes, but is not limited to, the following considerations:
Pre-planned or instant handwriting: If an addition was pre-planned, a fraudster can reserve a place for it and even retain the implement used to write the text, making the addition seamless. This type of alteration is harder to detect.
Paper characteristics and the time gap between writing the initial entry and alteration: Typically, fresh inks penetrate the paper more deeply, leaving traces on the reverse side of the document.
Ink type and characteristics: Since ink pigments exhibit different effects under various light sources, you can detect a false entry using lighting and filtering techniques.
Writing surface: If a fold is present where an addition occurs, you can see disruptions in the stroke, as well as shifts in the pen direction.
Using imaging devices to detect alterations
Tiny changes in handwritten documents may go unnoticed by the naked eye. Yet, they often become discernible through imaging tools that employ different light sources and magnification features. Video-spectral comparators fall into this category.
Regula offers an array of advanced equipment for forensic document examination. For example, the dual-video spectral comparator Regula 4308 stands out from the competition with its exceptional features. Equipped with two optical systems and a movable object stage, the device can examine documents of any size.
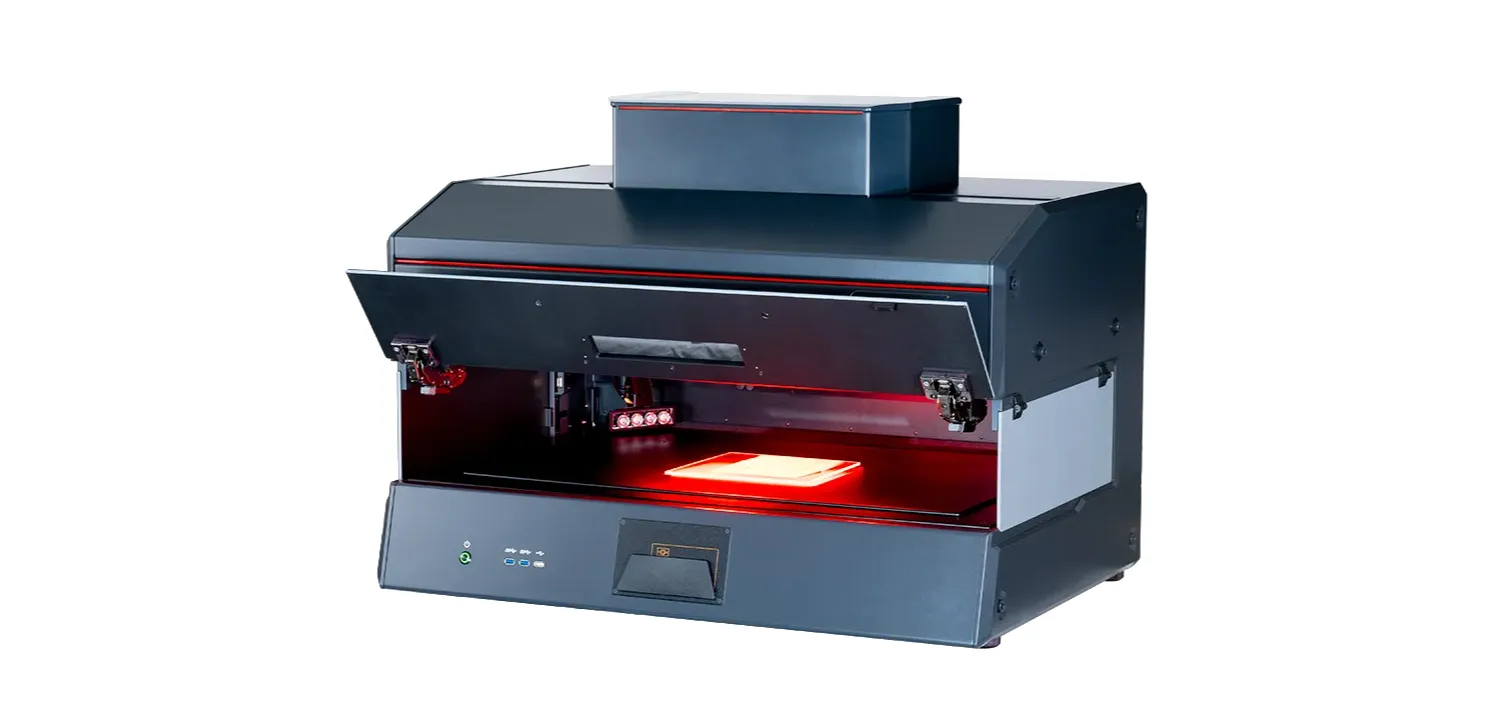

Regula 4308.
This device is a great assistant in the day-to-day operations performed by forensic experts. Specifically, the inclusion of a high-resolution spectrometer, hyperspectral imaging module, optical magnification up to 320X, and various light sources, make it the perfect tool for non-destructive examination of altered documents. By the way, here are more Regula devices for advanced examination.
Now, let's delve into the forensic document examination techniques for inspecting alterations in detail using this paper check as a test object.

This test object includes at least two additions that are hard to detect under visible light.
Narrowband light sources
Observing a questioned document under different lighting conditions can reveal forged strokes or lines, using the infrared luminescence effect. This can indicate the use of ink other than the original, suggesting the presence of an alteration.
To check the consistency of ink color throughout the entire document, examiners can use specific narrowband light sources, such as visible violet or yellow, or combine several sources with various wavelengths. By using additional light filters, it’s possible to alter light transmission characteristics to allow only a certain range of wavelengths to pass.


Examining handwritten documents under narrowband light sources helps detect alterations made with different types of ink. For example, this paper check (a test object intentionally made by Regula forensic experts for demonstration) includes two additions: a digit “1” and the word “teen,” which turns $7000 into $17,000 (seventeen thousand dollars). Not detected under visible light, these additions reveal themselves under IR, at 395 and 635 nm, respectively.
The range of wavelengths of narrowband light in the Regula 4308 is 395-700 nm. The 12 light sources can be easily switched using the desktop interface. Additionally, you can zoom in or out through the document to closely examine individual strokes and lines.
Hyperspectral imaging
This method uncovers more details about the inks used in an altered document. Based on hyperspectral analysis, it indicates the presence of inks with varied characteristics in one stroke or line.
In the Regula 4308, the hyperspectral analysis module allows users to observe the strength of the reflected signal of a specific light wave at a certain area of the document, indicating the amount of light waves reflected by the surface. This is significant, because inks used to alter handwritten text may reflect light differently.
To facilitate examination, the comparator can automatically capture a series of images in the range of 395-1000 nm; the device’s camera takes a shot every time there is a shift (with a 1 nm step as a minimum) along the spectrum. The smaller the step, the higher the precision of measurements. For example, with a 5 nm step, the results may look like 395 nm, 400 nm, 405 nm, and so on.
With this method, you will get a set of images that can be turned into graphs showing the strength of the reflected signal under various illuminations. For a detailed comparison, you can generate a pair of graphs (or more) for different strokes, including original and questioned/altered lines.

During hyperspectral analysis, the device measures the strength of the reflected signal from lines or strokes in a handwritten text using images captured under different lighting conditions. The results are presented in graphs. The differences between these graphs highlight additions.
Note: Usually, the amount of ink throughout the writing is uneven due to many factors, including the characteristics of the writing implement. That’s why original lines in the handwritten piece sometimes may also show different strengths of the reflected signal during hyperspectral image analysis. However, this difference is not significant.
Spectral analysis of ink characteristics
A high-resolution spectrometer is a multi-purpose instrument for measuring and comparing color characteristics, and is capable of performing various tasks. The tool also comes in handy for measuring the color characteristics of inks when examining handwritten texts. The measurements are shown in color-coordinated graphs, making even subtle differences visible that might not be detected by the naked eye.
Different inks reflect light differently. When a piece of text looks suspicious, the spectrometer can be switched to a specific mode that measures the reflection of electromagnetic radiation. If there is a significant variation in measurements between stroke samples in the document, it indicates alterations have been made.
Here’s how it works.
First, you need to place the specific part of the document in the spectrometer. 20X magnification is optimal for handwritten questioned document examination.
How to prepare the device for operation
For accurate results, preparing the device is essential before use. This involves capturing two references: complete darkness and white light.
To obtain the dark reference, the spectrometer turns off the light sources. The test object, an etalon of white color, is placed in the spectrometer's field of view and serves as a color reference to help set up the device.
The adjustment lasts a few seconds while the spectrometer captures two shots in both light and dark conditions.
Once the device is ready to use, you can start the examination. By shifting the spectrometer camera from stroke to stroke, you will see the graph showing the strength of light reflection in different places of the document. The movable object stage in the Regula 4308 allows for smooth adjustments. Taking shots of these pieces enables you to compare the graphs further.
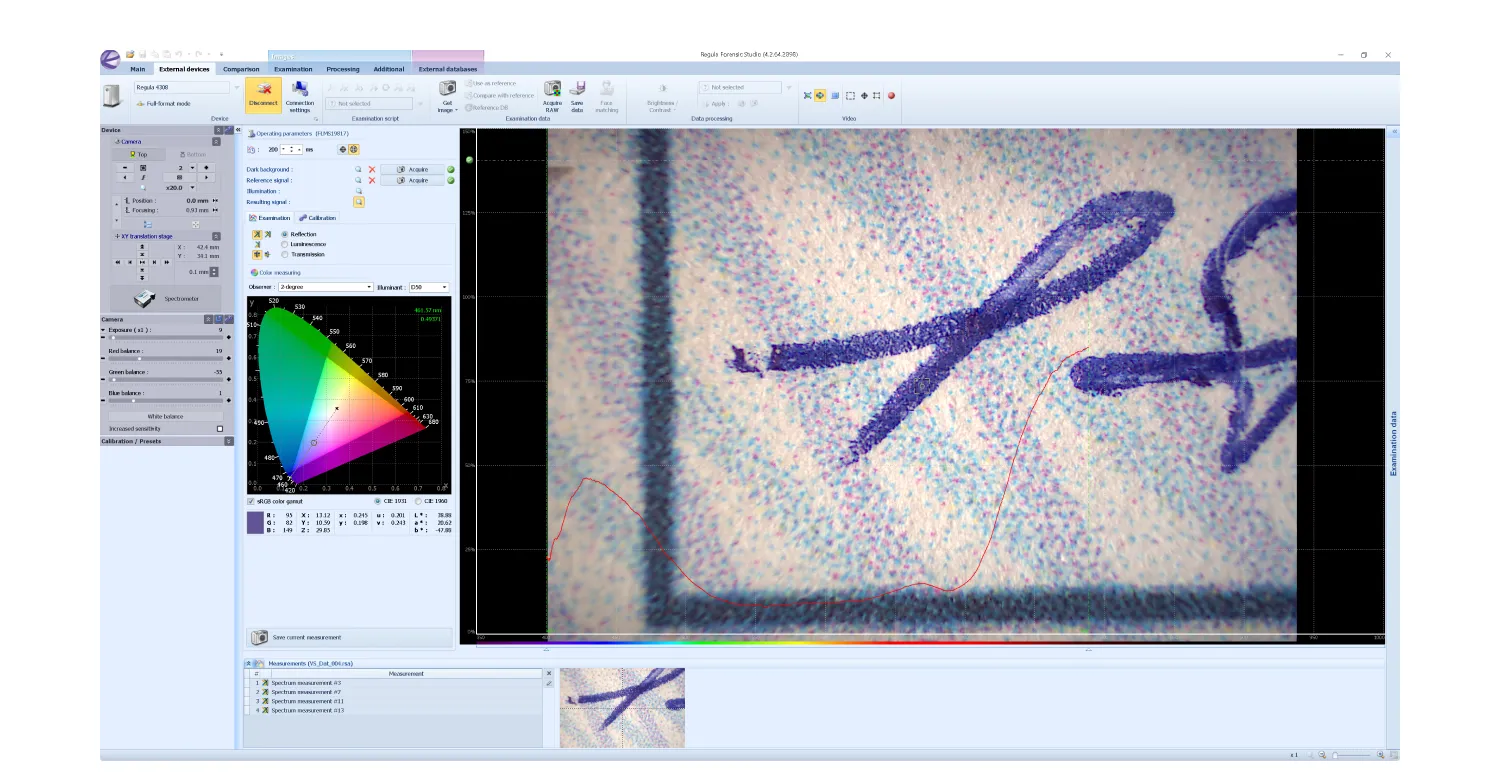
Once you place an object in the focus of the device, the graph (red) shows the strength of light reflection by inks in this stroke. You can save the results for further comparison.
Then, you can cross-reference the graphs to reveal any differences between them. Usually, experts compare the graphs obtained from various sections of the strokes, both those in question and those not, to conduct further analysis on the two groups.

You can view the graphs corresponding to the parts of texts you analyze one by one, or compare them to determine alterations.
For strokes written with the same inks, the measurements are identical. With the Regula 4308, you can sum up several measurements to get two graphs based on average values for comparison.
You might also like What Is 3D Reconstruction and What Tasks Does It Solve in Forensics?
Drawing up a report when using non-destructive methods
Last but not least, after carefully collecting all the measurements, the forensic expert must create a detailed report summarizing the results of the examination.
When preparing the report, the expert must indicate the presence or absence of alterations in the handwritten document they examine. This judgment should be well-informed and accurate; therefore, the report should always include an evidence section with images and graphs taken during the examination.
Along with our other devices, the Regula 4308 is integrated with Regula Forensic Studio. With a wide range of examination, comparison, and processing functions, the software also streamlines report generation.
When you examine questioned documents with this video-spectral comparator, you can also save a lot of graphic data. It’s easy to add all the necessary data to the report: for example, image capture conditions, sample photos under different light sources, and a plethora of graphs showing the different nature of the inks used.
Advantages of non-destructive document examination methods
Wrapping up, let’s take a look at the major benefits of using non-destructive methods for identifying alterations in handwritten documents:
No damage to the document: The original document’s properties and characteristics don’t change during the examination. This aspect is critical when authenticating pieces of evidence or documents of historical significance.
No restrictions for repeated inspections: The number of repeat examinations by other experts and forensic laboratories is not limited. If the results are vague, the document can be rechecked. Since the object remains the same, other specialists may start the examination from scratch.
Extensive functionality: The range of available tools includes narrowband light sources, as well as hyperspectral and spectral analysis, allowing for precise results.
A wide range of application scenarios: Non-destructive methods provide a quick, useful, and careful way to analyze different documents, including fragile ones.
Detection of different types of fraudulent alterations: Thanks to the wide range of light sources and filters, many types of alterations can be detected.
Easy report generation: Non-destructive methods involve the use of a video-spectral comparator. Consequently, all measurements in the form of graphs and images are readily available for an expert. These findings may be included in a report as they are, making report generation less time-consuming and effort-intensive.