Many businesses—from ecommerce to banking—need to check their customers’ age.
The specific use cases vary, but the tools and legal requirements are increasingly well established.
In this article, we’ll break down the types of age verification technologies, how they differ, and when to use (or avoid) each one to keep the process secure, compliant, and smooth.
Subscribe to receive a bi-weekly blog digest from Regula
The major idea behind age verification
Age verification is the process of confirming that a person meets the legal age to access restricted products or services. Importantly, in most cases, the real age doesn’t need to be revealed—just a confirmation that the person is “not younger than” the required age.
This includes alcohol, tobacco, energy drinks, gambling and gaming platforms, pharmaceuticals, adult content, firearms, and more.
Each country or jurisdiction defines what is considered age-restricted—both online and offline—and sets minimum age limits, usually between 16 and 21.
There are many ways to verify age, from a simple self-declaration (like “Are you 18 or older?” pop-ups) to presenting an official ID document.
Real-world example: In the UK, retailers follow a voluntary policy called Challenge25. It requires staff to ask for ID at checkout or delivery if the buyer appears under 25. Accepted documents include passports, driver’s licenses, or other valid IDs. The legal minimum age to buy alcohol or fireworks in the UK is 18.

In the UK, young people can use a CitizenCard—a domestic ID document—as valid proof of age when buying restricted goods.
Globally, both regulators and identity verification vendors use different terms to describe age-checking methods. This inconsistency can confuse businesses and sometimes lead to unrealistic expectations.
Let’s clarify the key terms used in this space.
Age verification terms: What is the difference?
There are at least four common approaches to age verification. Let’s start with the most basic:
#1 Age gating
Age gating limits access to a website, app, or content if a user is under a certain age. These “age gates” usually block content until the person confirms they’re an adult.
This confirmation often takes the form of a pop-up asking for a date of birth, or a checkbox agreeing to the terms of use. Because it relies on self-declaration, it’s easy for minors to bypass.
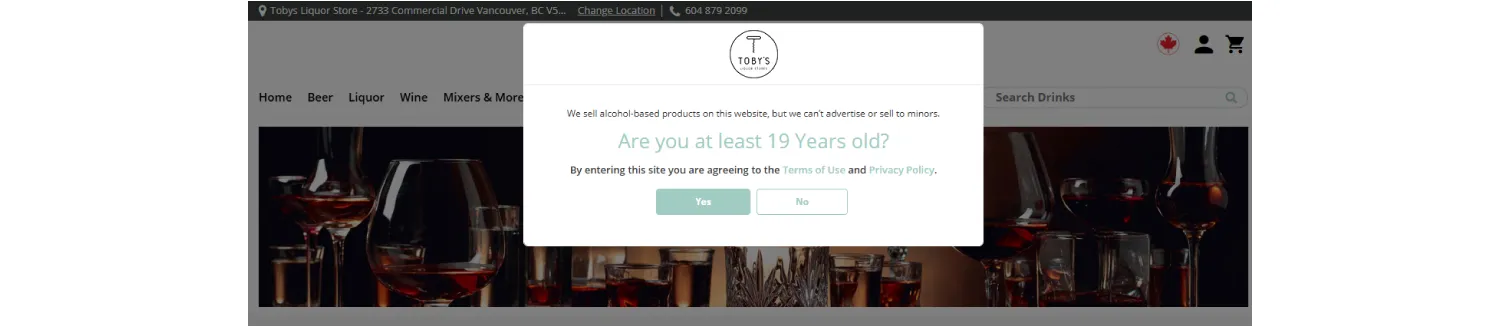
In Canada, the minimum legal age to buy alcohol is 19. This pop-up from a local store is a typical example of age gating. Source: www.tobysliquorstores.ca.
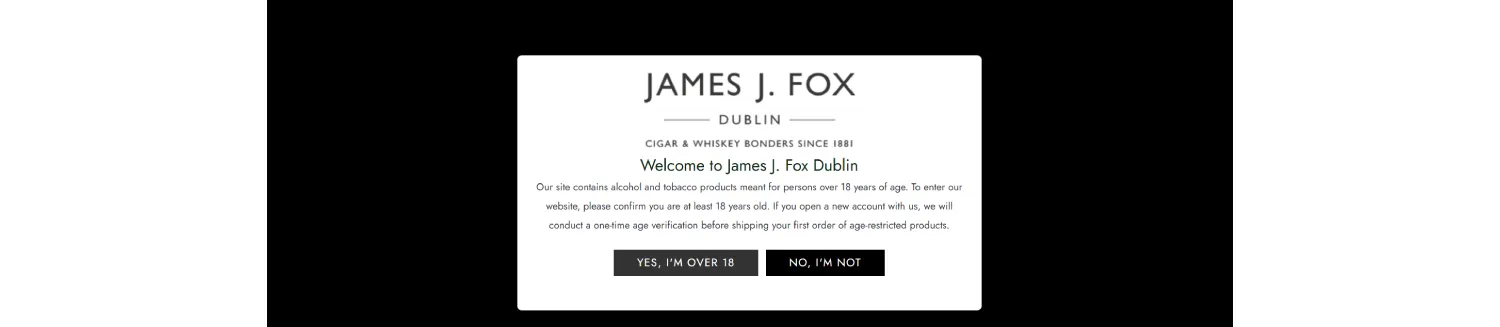
On this Irish tobacco site, the entire page is hidden until users confirm their age. No real check is required—just one click. Source: jamesfox.ie.
Age gating is considered the least reliable method of age verification. Still, it helps websites show basic compliance. The actual check often happens later—when age-sensitive goods are delivered, and the courier verifies ID in person.

With this UK fireworks store, delivery drivers may be required to check the customer’s ID face-to-face.
#2 Age estimation
Age estimation uses images or video of a person’s face to estimate their age. This method is widely accepted by regulators and labs, including the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
Unlike age gating, age estimation is algorithm-based and fully automated. It relies on biometric technology that analyzes facial features to calculate age.
According to NIST, age estimation methods can support various tasks, such as:
Verifying that a person is over 18, 21, or another legal age (e.g., for buying restricted goods).
Confirming that a person is under a certain age (e.g., for entering a teen-only chat room).
Collecting demographic statistics (e.g., the age of moviegoers).
Powering digital ads based on age profiles.
Checking if a passport photo is recent.
Estimating the age of undocumented individuals, refugees, and asylum seekers.
NIST’s Face Analysis Technology Evaluation outlines three approaches to age estimation:
Direct estimation: An image or video is analyzed to estimate the person’s age.
Reference comparison: The user’s image is compared with a reference image of known age.
Threshold evaluation: The algorithm estimates how likely the person is to be above a specific age (e.g., 21).

Algorithms can either output an estimated age, compare against reference images, or check if someone is likely to be above a defined threshold.
Age estimation can be used during remote onboarding, at payment points, or even onsite.
NIST’s view on age verification vs. age estimation
NIST clearly distinguishes between the two:
Age verification gives yes/no answers—whether someone is above a set age (like 18 or 21). The result is a boolean value: true or false.
Age estimation provides a numerical result—for example, 23.7 years—using AI to analyze facial features.
#3 Age verification
Following NIST’s distinction, it makes sense to treat age verification as a separate method from the broader term used earlier. In addition to analyzing a user’s face, this approach can rely on authoritative sources to detect someone’s date of birth and calculate the difference between that date and the current date.
Authoritative sources typically include government-issued ID documents, official databases, and records.
In practice, age verification often follows a standard identity verification flow involving both document and biometric checks.

Interestingly, some countries issue special versions of domestic ID documents specifically for age verification. These often have a unique design and may display not only the date of birth but also the dates when the holder turns 18 or 21. This simplifies on-site age checks—for example, at bars—where employees without specific training must quickly and accurately confirm that a guest is old enough to buy drinks.

In the US, driver’s licenses for minors often have a portrait-oriented layout and display three key dates related to the holder’s age.

Several Australian states issue special domestic IDs that serve as official proof of age.
#4 Age assurance
Unlike the practical methods described earlier, age assurance is a legal requirement now being introduced in many countries. Its goal is to ensure that users or customers are over a key age threshold—typically, 18, 21, or another regulated age.
This may be confusing, as both age verification and age estimation serve the same purpose. However, the key difference is that age assurance is, first and foremost, a framework—not a method—built around compliance, online safety, and content gating principles.
The mechanisms companies must use under age assurance requirements to assess a customers’ age differ from country to country. As a result, age assurance can refer to a variety of verification methods depending on the jurisdiction.
For example, in the UK, Ofcom—the communications regulator—has defined strict technical requirements for effective age assurance under the Online Safety Act. Methods like self-declaration (i.e., age gating) are not considered compliant. Instead, acceptable approaches include mobile network operator age checks, credit card verification, and digital identity services for age estimation methods.
In Australia, regulators include age inference as one of their age assurance techniques. This approach is also referenced in the ISO/IEC FDIS 27566-1 standard.
Technically, age inference means estimating a person’s age based on verified facts that indirectly suggest their age or age range. These facts must come from trustworthy sources and be confirmed to relate to the correct individual.
Examples of such sources include:
School enrollment records
Credit card ownership
Account tenure
Usage behavior patterns
Notably, age inference excludes both direct age verification (using government-issued IDs) and age estimation (based on facial biometrics).
How Regula can help you verify customers’ age
As a 100% in-house developer of identity verification technologies, Regula offers multiple solutions to meet your age verification needs:
Age verification via ID document checks using Regula Document Reader SDK—an on-premise solution powered by a database of 15,000+ ID templates from 252 countries and territories. It combines OCR, document authentication, and ID liveness checks.
Age estimation through facial analysis with Regula Face SDK—a robust tool for deep selfie verification, including passive or active liveness detection and face matching. It enables instant age estimation and protects against fraud like deepfakes, printouts, and screen replays.
Age assurance via an orchestrated workflow with Regula IDV Platform—a unified, single-vendor solution that brings together all Regula SDKs to manage the full customer identity lifecycle in one place.
Let’s talk about your goals and explore how we can help—book a short intro call today.