At times, identity verification resembles the wide variety of Lego bricks. There are basic bricks, without which you can’t build castle walls. Missing one brick results in the risk of the whole construction collapsing. There are also fancy bricks, such as flags, or even a dragon to sit on the wall. You can go without them—but it’s definitely less fun.
In this analogy, face recognition isn’t a basic brick for just any identity verification workflow—save for surveillance, perhaps. However, it definitely adds an additional layer of security for most businesses.
In this post, we’ll discuss how a facial recognition process works in identity verification, and cover scenarios in which it’s 100% worth a shot.
Let’s get started.
What is facial recognition?
Perhaps you've boarded a flight using just your biometric data, entered a secured area after a camera identified your face, or even paid for groceries simply by looking into a camera. These scenarios highlight the increasing use of facial recognition in everyday situations.
Face recognition is a biometric technology that involves identifying or verifying an individual based on their unique facial features. The principle is simple: once you have an image of an individual, the technology searches through a database of faces to find whether there’s a match. In our example with payments, the bank system literally looks through all their clients' profiles to identify the one who’s in front of the cashier at the moment.
This search is performed on a one-to-many basis (1:N): one face is compared against numerous other faces, with N referring to the size of the database.

Typically, face recognition yields a similarity rate rather than a binary match or no-match result. This is because faces are subject to variations such as changes in expression, capture angle, makeup, accessories, and age, among other factors.
Is face recognition the same as face matching?
As for face recognition and face matching, they are different procedures from a business standpoint, even though one is based on the other.
Face matching here refers to face verification that is performed on a 1:1 basis. It’s when you have an ID document and a selfie of a person, and your goal is to confirm that it is the same person in the two photos.
On the other hand, facial recognition involves identifying a specific individual within a database using a single photo. If you need an alternative term for face recognition, then it’d be “face search” or “face identification."
💡The field of biometrics is rich in technologies, techniques, and corresponding terms. We’ve even published an explainer to help you understand the differences between the most widespread items.
Subscribe to receive a bi-weekly blog digest from Regula
How does facial recognition work?
In short, a facial recognition system analyzes and compares facial features to identify a person. But let’s have a closer look.
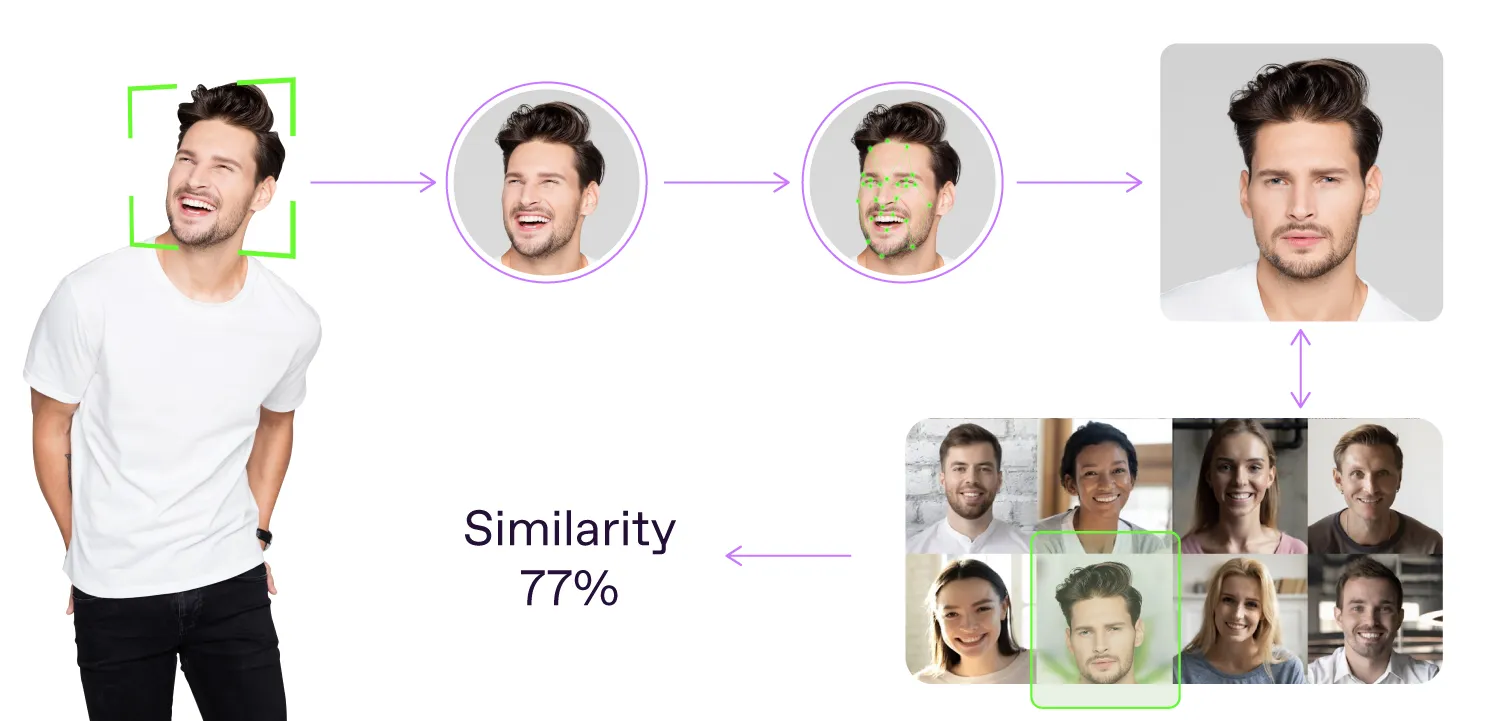
1. Image capture. The process starts with capturing an image of a person’s face. It may be a live capture made in real time (during online onboarding or at a border crossing), or it can also be a photo or video uploaded from a user’s device.
2. Face detection. After the image is obtained, the facial recognition system searches for and detects a face in it. This stage's main purpose is to distinguish the face from the background. Therefore, the system focuses only on locating and isolating the face in the picture, ignoring everything else.
3. Facial feature extraction. At this stage, facial recognition technology analyzes key facial features, also known as facial landmarks. These landmarks are specific points on the face, such as the distance between the eyes, the width of the nose, the shape of the jawline, the position of the cheekbones, etc.
4. Creation of facial templates. The extracted facial features are then converted into a mathematical representation or a template. This template is a digital version of the face, which the system will use for comparison.
5. Face matching. Next, the facial recognition system compares the newly captured facial template with templates stored in a database to find a match.
6. Decision. Based on the results, the facial recognition system provides a verdict, stating whether the face is verified or identified.
What is a facial recognition algorithm like in identity verification?
In IDV, a basic face recognition flow is pretty much the same. It is based on three major steps: detection, analysis, and comparison. Ideally, there should be one more: image quality assessment.
Detection: The system identifies the presence of a face in an image or a video using algorithms that can detect facial features, such as eyes, nose, and lip corners. Once the face is detected, the algorithm fetches an image of it for further processing.
Quality assessment: Advanced identity verification solutions recommend implementing this step to enhance the reliability of face recognition. Image assessment ensures the image meets specified quality standards, and there are no occlusions like face masks or glasses. Still, this step may be omitted if the image quality is assured, such as when photos are taken by staff in a controlled environment rather than being submitted by users online.
Analysis: By identifying unique characteristics of the face, the software creates a distinct facial signature, or descriptor, for each individual. These descriptors are like points in space. For images of the same person, they are close, and for images of different people, they are far away. The closer the descriptors are, the higher the similarity.
Comparison: The obtained descriptor is then compared against a database of known faces. Based on the comparison results, the facial recognition technology determines whether the provided facial image has a significant similarity rate with any existing entry in the database. Depending on the thresholds set within the face recognition solution, the obtained value can be interpreted as a match or no match.
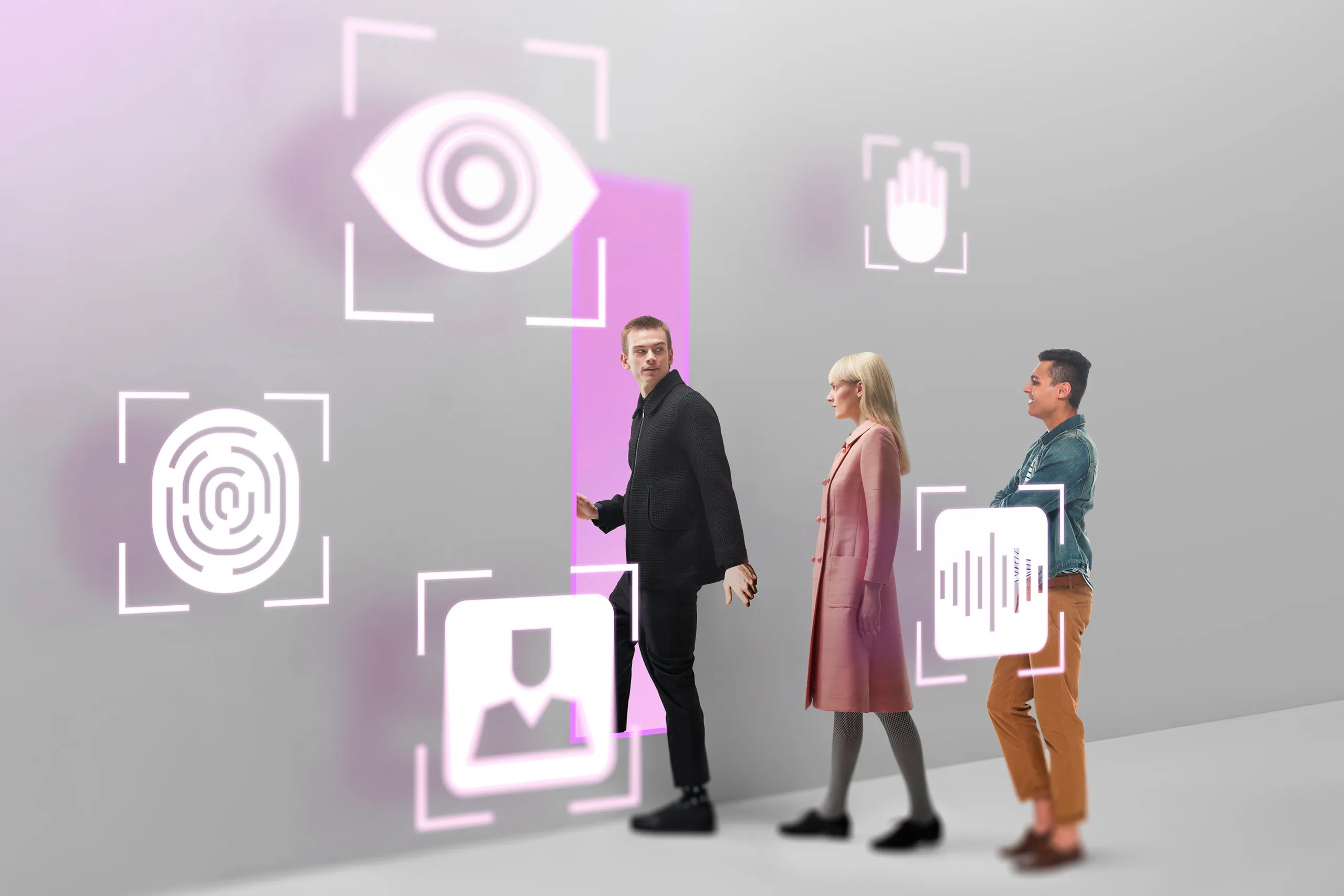
Where is facial recognition used?
Facial recognition is widely used in various use cases, from digital banking to law enforcement and more. Streamlining processes, enhancing security, and improving user experience, this technology has become critical in many sectors.
For example, facial recognition is now a key element in access management and authentication processes. Organizations use the technology to grant employees and visitors secure access to their premises, reducing reliance on physical keycards. Many smartphones and laptops use facial recognition to unlock devices, replacing passwords and PINs with biometric authentication. This creates more convenience and security for users.
Airports and border control authorities use biometric facial recognition to verify travelers’ identities. Automated systems can match passengers' faces against their passport photos, speeding up security checks and reducing the need for manual verification.
In turn, banks and financial institutions use facial recognition technology for secure access to online banking apps, which helps protect accounts from unauthorized access and fraud. In some regions, facial recognition is used to authorize and fulfill payments, thus replacing traditional methods such as credit cards.
Four examples of scenarios where face recognition is a game-changer
While some conventional applications of facial recognition technologies may smack a bit of Big Brother, there are plenty of recent use cases where it can work for a good cause. Here are four use cases where this technology makes a difference, either in security or in user experience:
→ Password recovery process. The vulnerability of knowledge-based authenticators, such as passwords, secret phrases, or even PINs, to theft by scammers is well-documented. With facial recognition technology, individuals can regain access to their accounts, preserving both convenience and security, by simply capturing a new selfie.
→ Entry/exit process during mass events. Managing the influx of attendees during large-scale events often creates various risks, from a tussle to get in first to presenting fake passes. When face recognition is turned on, attendees can simply look into the camera for identification, minimizing congestion at entrances and exits. This elevates the experience and also helps organizers accurately track attendance.
→ Security in the sharing economy. Whether it's ride-sharing platforms or accommodation rentals, integrating biometric facial recognition enhances authentication processes. The technology largely contributes to mitigating fraudulent activities and fostering a more trustworthy environment for both service providers and consumers.
→ Fighting gambling addiction. With facial recognition technology, individuals can voluntarily enroll in self-exclusion lists, effectively prohibiting their entry into casinos and betting venues. By leveraging facial biometrics, these programs provide guardrails that empower individuals to take control of their addiction and seek support for recovery.
What are the benefits of facial recognition?
As we wrote in another post, integrating a facial recognition component into your identity verification workflow is a great way to safeguard against unauthorized access to your systems, platforms, and even brick-and-mortar facilities.
After a customer confirms their identity, their facial biometric data gets included in a digital profile stored in the system. Then, when they need to verify their identity again, the system checks any new selfie they provide against this profile. If the new photo matches well enough, the system knows it's the same person, and grants them access.
But why opt for facial recognition technology over other authentication methods?
Given the prevalent risks associated with phishing, poor password hygiene, and social engineering practices, more companies are turning to a passwordless approach. Biometrics, particularly facial recognition, emerges as a promising solution for ubiquitous internet sign-ins.
So, if you need a summarized list of the main benefits of facial recognition, here it is:
Key advantages of facial recognition
Enhanced security and fraud protection. Facial features are unique. Unlike passwords, which can be stolen or guessed, face recognition significantly contributes to securing access to various accounts and systems. Thus, organizations can implement robust protection from identity fraud and theft.
Improved user experience. Facial recognition is fast, and it requires minimal action from the user. Users don’t need to invent and memorize complex passwords or carry physical tokens. All they need to do is simply look at the camera, and voilà —their identity is verified, and access is granted. This creates a smooth and seamless user experience, which is especially important in industries like Banking, Retail, and Travel.
Process automation and efficiency. Automated facial recognition streamlines identity verification in workflows such as online banking, airport security, customer onboarding, and more. This leads to faster transactions, reduced waiting times, and fewer bottlenecks. As a result, companies can benefit from improved and more efficient routine processes so they can focus on more crucial tasks.
Eliminating human error. Relying on facial recognition technology significantly decreases the so-called human factor. When checks are done automatically with the help of advanced IDV technologies, manual identity verification is no longer necessary, and the possibility of human error is reduced to a bare minimum.
Reduced operational costs. In the long term, facial recognition systems can reduce costs associated with managing passwords, PINs, and manual verification processes. Automated systems require less human intervention, lower maintenance costs, and reduce the time spent resolving security issues related to password resets or breaches.
Compliance with security standards. The pressure from regulatory bodies to adopt stronger security practices is only growing. In this situation, facial recognition helps organizations comply with even the strictest regulations for KYC (Know Your Customer) workflows.
What are the concerns about adopting facial recognition?
While facial recognition technology offers numerous advantages, it also has its potential drawbacks. Actually, some of them are just a mirror image of the benefits.
Privacy concerns
Facial recognition raises significant privacy issues, as some individuals feel uncomfortable being monitored or sharing their biometric data. For example, surveillance cameras in public spaces may give people concerns about civil liberties and personal data collection without explicit consent.
Data security risks
Storing biometric data, such as facial images, poses probably the most serious security risk. Unlike passwords, which can be changed, facial biometric data is permanent. If this highly sensitive data is compromised through a data breach, it could lead to identity theft and sophisticated fraud, including deepfakes and other AI-generated content.
Bias and inaccuracy
Facial recognition systems have repeatedly been shown to have accuracy issues in identifying individuals of different ethnicities, genders, or ages. This bias can lead to false positives or false negatives. As a result, people can suffer from discrimination or wrongful identification. In law enforcement settings, for example, such inaccuracies may have grave consequences.
Cost of implementation
The initial cost of implementing a facial recognition system can be relatively high. It requires investment in software, hardware, and system integration, as well as ongoing maintenance and updates. For smaller organizations, this can be quite a challenge.
Regulatory challenges
As the technology deals with highly sensitive biometric data, facial recognition is subject to growing regulatory scrutiny. Some regions have already banned or heavily regulated its use due to concerns about misuse and overreach. Therefore, adopting the technology may require navigating complex legal considerations.
Public resistance
Public opinion on facial recognition is often divided, with many individuals expressing discomfort or opposition to its use in daily life. This can lead to pushback from customers or employees, potentially affecting trust in the organization implementing the technology.
Dependence on environmental factors
The effectiveness of facial recognition can be significantly impacted by environmental conditions. Poor lighting, camera angles, insufficient image quality — all these factors may hamper biometric checks and lead to inaccurate verification.
Why integrate facial recognition with other authentication methods?
Facial recognition is a powerful IDV technology. However, it becomes most effective when integrated with other authentication methods.
Now that sophisticated identity fraud, for example using deepfakes, has become an everyday reality for every second business around the world, facial recognition seems to be insufficient without liveness detection. Liveness detection is a robust check to ensure that the biometric data is being captured from a live person, not from a photograph, video, mask, etc. This is crucial in preventing spoofing attacks, in which fraudsters attempt to bypass the IDV system by presenting a static image or pre-recorded video.
Advanced liveness detection technologies can track eye movement, trace changes in light reflection on the skin, or detect slight head movements. These nuances help determine if the person in front of the camera is real.
Additionally, it is highly advisable to introduce a multi-factor authentication (MFA) approach. It combines facial recognition with other methods such as one-time passwords, fingerprint scanning, or even behavioral pattern tracking. This layered approach minimizes the risk of falling victim to identity fraud, and provides a backup method if one check fails.
How to implement facial recognition in your workflows
Building a reliable facial recognition system requires significant effort. At a minimum, you must:
Develop a face detection algorithm that reliably identifies faces.
Train descriptor comparison algorithms to ensure accurate results when comparing two images.
Create a scalable system capable of searching for unique faces among a vast number of images.
While it's possible to undertake this work in-house, it demands considerable time, and might not align with your company’s core expertise.
Regula has been honing its competence in identity verification for more than 30 years. By integrating our solutions, which feature a pre-configured facial recognition component, you can achieve the quickest time-to-market without sacrificing reliability.
Regula Face SDK enables biometric verification with rapid and accurate facial recognition, liveness detection, and face matching and identification capabilities, which are functional across any user device. This ensures that only live, authenticated individuals get access to your services, providing you with unparalleled security and peace of mind.