A user signs up for a banking app. A digital nomad fills out an application form to obtain an electronic visa. A new employee gains access to corporate services through new credentials—email and password.
All these people interact with online systems using their accounts, often after confirming their identity through physical documents and/or biometrics.
These systems, controlled by companies, are complex and fragmented. Typically, they consist of a patchwork of identity verification (IDV) solutions, data sources, storage systems, customer management platforms, HR systems, and legacy infrastructure—all essential for smooth and secure operations.
To maintain and protect these digital systems effectively, especially in regulated or high-risk industries, businesses are shifting to platform-based frameworks that support the full identity lifecycle.
In this article, we’ll look at each stage in a user’s journey—from onboarding and verification to ongoing management and offboarding—to see how platform-based IDV solutions can streamline and strengthen each step.
Get posts like this in your inbox with the bi-weekly Regula Blog Digest!
What is identity lifecycle management?
Identity lifecycle management (ILM) is a framework of processes and technologies used to manage user identities from creation to deletion. An identity—whether of a customer, employee, or any other user—is defined by unique characteristics, such as biometrics and personal details, along with activity logs, transactions, and other behavior within your system.
In practice, ILM brings together several large tasks that often exist as standalone processes or policies:
Issuance and deactivation of accounts or credentials
Identity and access management
These processes typically follow a user’s journey through the system:
| The main stages in the digital user journey | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1) Onboarding | 2) Authentication & transaction | 3) Offboarding |
| A user signs up and confirms their identity through document and/or biometric checks. | After being granted access to specific services or transactions, the user interacts with the system: e.g., transfers funds, pays, updates data, applies for a loan, etc. | The user leaves the system, and their account is deactivated. |
This is a simplified model meant to provide a general overview. In reality, users interact with systems in many ways. For example, a person might authenticate using a different device from the one used during registration. They might forget their credentials and get locked out after too many login attempts. Unfortunately, some people might try to deceive the system through impersonation or identity theft.
A well-managed identity lifecycle helps detect errors or suspicious activity within registered accounts. It prevents unauthorized access, data breaches, and fraud, while ensuring compliance with industry regulations like privacy laws, Know Your Customer (KYC), and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) rules.
To achieve this, companies must focus on four core areas:
Secure onboarding
Effective identity management
Up-to-date regulatory compliance
Fortunately, modern IDV platforms are built to manage this full lifecycle. These all-in-one solutions securely onboard users, verify and monitor identities in real time, and orchestrate identity data across the user journey.
Major pillars in identity lifecycle management
Let’s explore the key phases of the identity lifecycle where platform-based IDV solutions can make a difference.
1. Onboarding and orchestration of identity verification workflows
As the first stage in the identity lifecycle, onboarding is also one of the most critical. This is where businesses integrate a new user into their digital environment—and must ensure that that user is a real, legitimate person eligible to access their services.
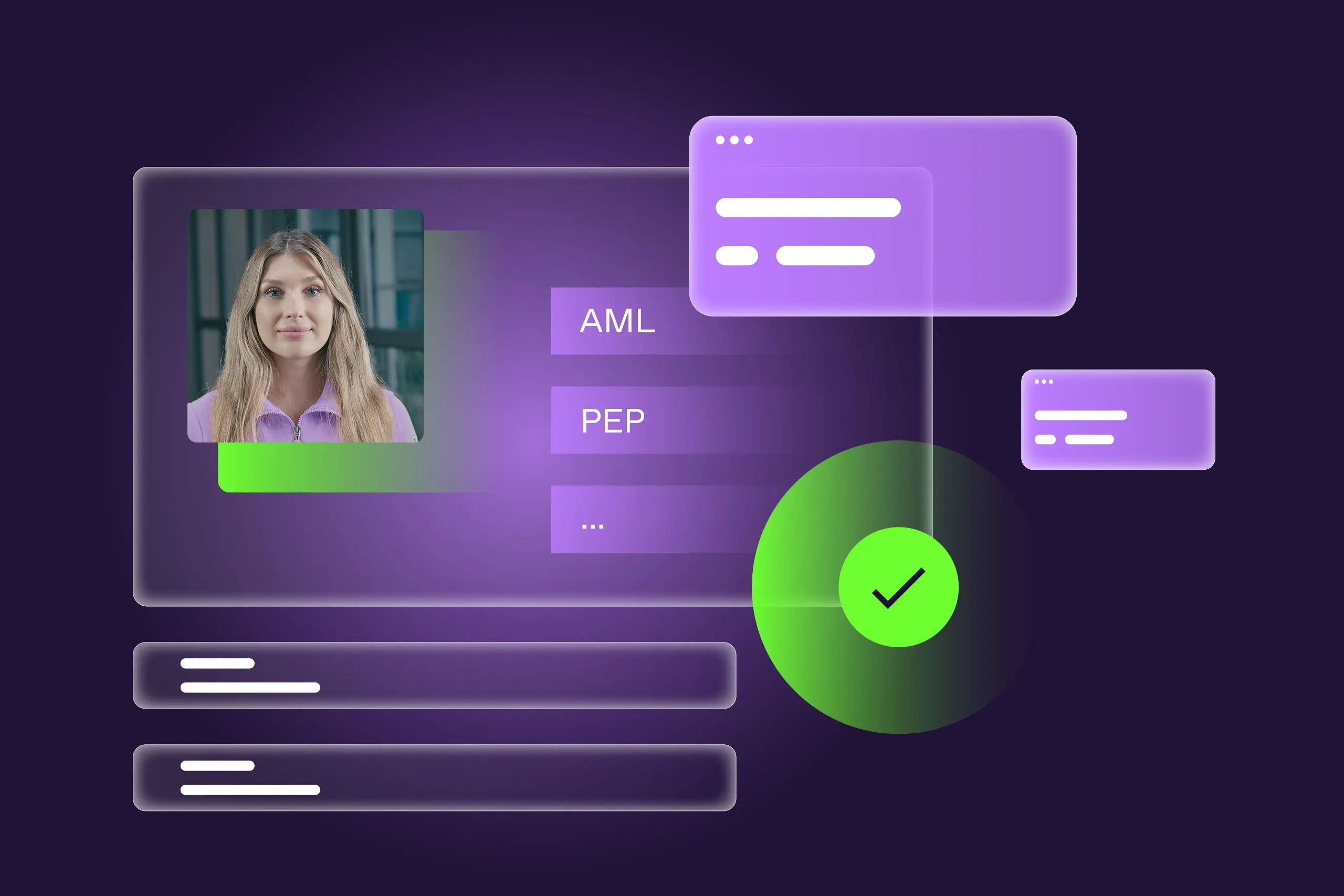
That’s why effective onboarding always begins with identity verification. In regulated sectors such as banking or aviation, this typically includes KYC and AML checks. These often involve:
Collecting identification data such as name, address, date of birth, and a photo-ID document that includes biometrics.
Verifying the authenticity and validity of this data—usually, using document authenticity checks and selfie matching.
Screening users against AML or Politically Exposed Person (PEP) databases.
These steps form the foundation of trust before any access is granted. They help detect fraudsters attempting to impersonate someone else by using fake IDs, deepfake selfies, etc.
To automate the process and make it easier for customers across locations and demographics, workflow orchestration is essential. It allows businesses to set up step-by-step user onboarding activities based on the user’s initial input. These may include, but are not limited to:
The type of document they present. Is it chip-enabled or machine-readable only?
User location. Which checks are allowed or required (e.g., passive vs. active liveness detection, age verification, etc.)?
Legal status. Is proof of identity enough, or are additional documents like proof of address needed?
The purpose of the interaction. Is the user simply signing up, or performing a high-risk action such as applying for a loan?
Custom workflows can also integrate additional data sources (like watchlists or government databases), devices (smartphones, self-service kiosks, etc.), and procedures (manual ID checks, video interviews, etc.)—tailoring the journey to both business needs and user context.
2. Ongoing monitoring and identity management
Once a user is successfully registered, they gain access to various activities and transactions based on their permissions.
At first glance, continuous oversight might seem unnecessary until something suspicious happens. However, the importance of ongoing monitoring shouldn’t be underestimated.
In regulated sectors, businesses typically apply customer due diligence procedures, which include assigning each user a risk level:
Low
Moderate
High
Based on the risk level, different checks are applied. For instance, in banking, customers with low-value funds in standard jurisdictions may be classified as low risk, while those appearing on PEP lists are automatically categorized as high-risk. As a result, low-risk users go through standard IDV checks, while high-risk individuals may also need to verify their source of funds or submit tax declarations.
Importantly, risk levels set at onboarding are not static. A user flagged as legitimate could still pose risks later—for example, if their average transaction amount starts to increase significantly or if they apply for a long-term visa for the first time. That’s why ongoing monitoring is a required policy for users in all categories.
There are additional threats to take into consideration, such as identity fraud, account takeover, or legitimate accounts being misused for illegal activities like smurfing.
Ongoing monitoring typically includes:
Perpetual KYC reviews.
Real-time fraud detection.
Transaction analysis.
Alerts for changes in a user’s risk profile.
Beyond its security value, this approach supports compliance. This means keeping only accurate and valid information in the user profile—no obsolete IDs, outdated addresses, or obsolete job titles—and performing required checks, such as age verification, when triggered by new regulations.
Monitoring also generates a digital trail for each user, including identity checks and activity logs. These records can be used to prepare reports that demonstrate adherence to anti-fraud and privacy regulations.
3. Offboarding and account deletion
The identity lifecycle ends with offboarding—when a user leaves the system, either voluntarily or due to policy violations. For example, an employee may leave a company, or a customer might switch to a competing service. At this stage, their account is removed or suspended, access rights are revoked, and their digital identity is retired.
Offboarding is just as critical as onboarding when it comes to security and compliance. Poor identity and access management lifecycle at this stage can lead to serious risks. Inactive or “ghost” accounts may be exploited by unauthorized actors. For example, a former employee retaining access to internal systems could commit corporate espionage. Similarly, credentials that aren’t deactivated could fall into the wrong hands and result in data breaches or phishing attacks.
This phase also supports compliance with data protection laws, which often require personal data to be properly archived or deleted once a user leaves.
In some cases, offboarding may involve a final check to confirm the user’s identity before account closure. This step helps prevent unauthorized access or manipulation of someone else’s account, and ensures that all services, subscriptions, and data access are fully terminated.
How platform-based IDV solutions support the full lifecycle
IDV is often seen as just one of many checks that businesses run during customer interactions. In most cases, companies integrate IDV into their onboarding flow as a third-party component.
This approach makes sense for many use cases. For instance, ecommerce companies selling age-restricted products may only need to confirm a buyer’s age. Similarly, car dealerships might scan a client’s driver’s license only to complete the paperwork.
However, managing the full identity lifecycle requires a more holistic approach. This is especially relevant for enterprise-level organizations and companies in regulated sectors such as banking, insurance, telecom, etc.
Here’s how businesses can benefit from implementing full-scale IDV platforms:
Complete onboarding IDV checks
A standard IDV procedure includes document and biometric verification. This is a multi-step process that runs a series of authenticity checks.
Once a user scans their government-issued ID, the software reads the data from both the visual inspection and machine-readable zones, checks security features with a liveness check, and verifies the electronic chip (if available).
Next, the system requests a selfie and matches it against the portrait on the ID and/or an internal database of known users. Liveness detection is applied again to prevent presentation attacks or other fraudulent tactics.
In many cases, this flow combines technologies from different IDV vendors, such as Optical Character Recognition (OCR), liveness detection, age verification, and face matching. While these tools can work smoothly with proper integration, they often result in a fragmented backend that is difficult to manage.
Some companies also run watchlist screenings or other database-driven checks, such as phone number, address, or email verification. Without automation, managing this multi-source infrastructure may require manual effort.
A platform-based IDV solution solves these challenges with an all-in-one approach. It offers complete document and biometric verification, integrates with external databases, apps, and other identity lifecycle management tools, and applies risk scoring, automating most checks and cross-references. As a result, both your customers and your team interact with a single, streamlined automated onboarding workflow.
Case management and workflow orchestration
Advanced customization and feature flexibility are also key advantages of platform-based IDV solutions. Most include case management tools that allow fraud teams to review and resolve issues in one place.
These platforms let you create and automate tailored workflows across all stages of the user journey, for instance, skipping unnecessary checks for low-risk users or applying stricter controls for high-risk groups.
Some vendors, such as Regula, go further by offering pre-configured workflows for common KYC scenarios. This accelerates both implementation and day-to-day operations.
The platform also delivers a unified view of identity data throughout the lifecycle, serving as a single source of truth for onboarding and security teams. That’s a major upgrade from legacy setups where data is often scattered across multiple systems.
Built-in compliance
Any company that uses IDV when interacting with customers must stay compliant with relevant regulations—whether it’s KYC, AML, GDPR, CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), or age assurance laws. While these regulations come from the same general area, each demands specific checks and controls.
Platform-based IDV solutions that support identity lifecycle management often come with built-in compliance settings. These help companies meet regulatory requirements more easily, while keeping full control over sensitive data. They also simplify audit trail management and ensure proper data protection.
Perpetual KYC and activity monitoring
Platform-based IDV solutions often include built-in capabilities for perpetual KYC. This covers identity reverification, continuous watchlist screening, and real-time fraud analytics.
By integrating with other business systems—CRM platforms, transaction monitoring tools, and HR databases—the IDV platform can track changes and flag risk indicators, such as high-risk transactions or a new match on a sanctions list. It can also trigger predefined actions, like requesting additional documents or temporarily freezing an account.
With this setup, businesses gain a centralized system that continuously reflects the current identity status and risk level of each user, keeping data accurate, timely, and actionable.
An all-in-one, automated identity lifecycle management solution
Platform-based IDV solutions provide a fully controlled environment for IAM and security teams. In this setup, each customer has their own profile, which can be verified automatically or manually. These profiles store not only personal data collected during onboarding, but also activity logs—such as authentication attempts and in-system transactions.
This setup simplifies ongoing monitoring and the entire identity lifecycle management process, making it easy to update security policies quickly for all users or selected groups. It also removes the need to navigate fragmented interfaces, since all alerts, workflows, and systems are centralized in one place.
Orchestrate identities from first interaction to ongoing trust with Regula
Adopting an identity lifecycle management platform may feel like a milestone. But in today’s environment of sophisticated fraud, synthetic identities, deepfakes, and strict compliance requirements, it’s also a necessary and strategic step.
Regula IDV Platform helps you enhance security, stay compliant, and streamline operations with:
Complete identity verification using document and biometric checks in a single, seamless flow.
Database-driven checks, including AML and PEP screening, and validation against trusted global databases.
User data management and analytics for continuous monitoring.
Instant age verification to protect minors and ensure regulatory compliance.
Customizable workflows tailored to your business logic.
Smooth integration with your existing tech stack via flexible connectors.
A ready-to-use solution with fast setup, available for on-premise or cloud deployment.