Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is an essential technology with numerous applications across various industries. It is a versatile and reliable tool for automating data processing.
But OCR tasks in different companies always have some industry-specific nuances.
In this article, we’ll explore how OCR works in banking, which routine processes can be boosted by OCR, and what hurdles can reduce the technology's effectiveness.
What is OCR in general?
Just in case, let’s start with the basics. OCR pulls text from scanned documents and brings all the necessary data together, making it editable and searchable.
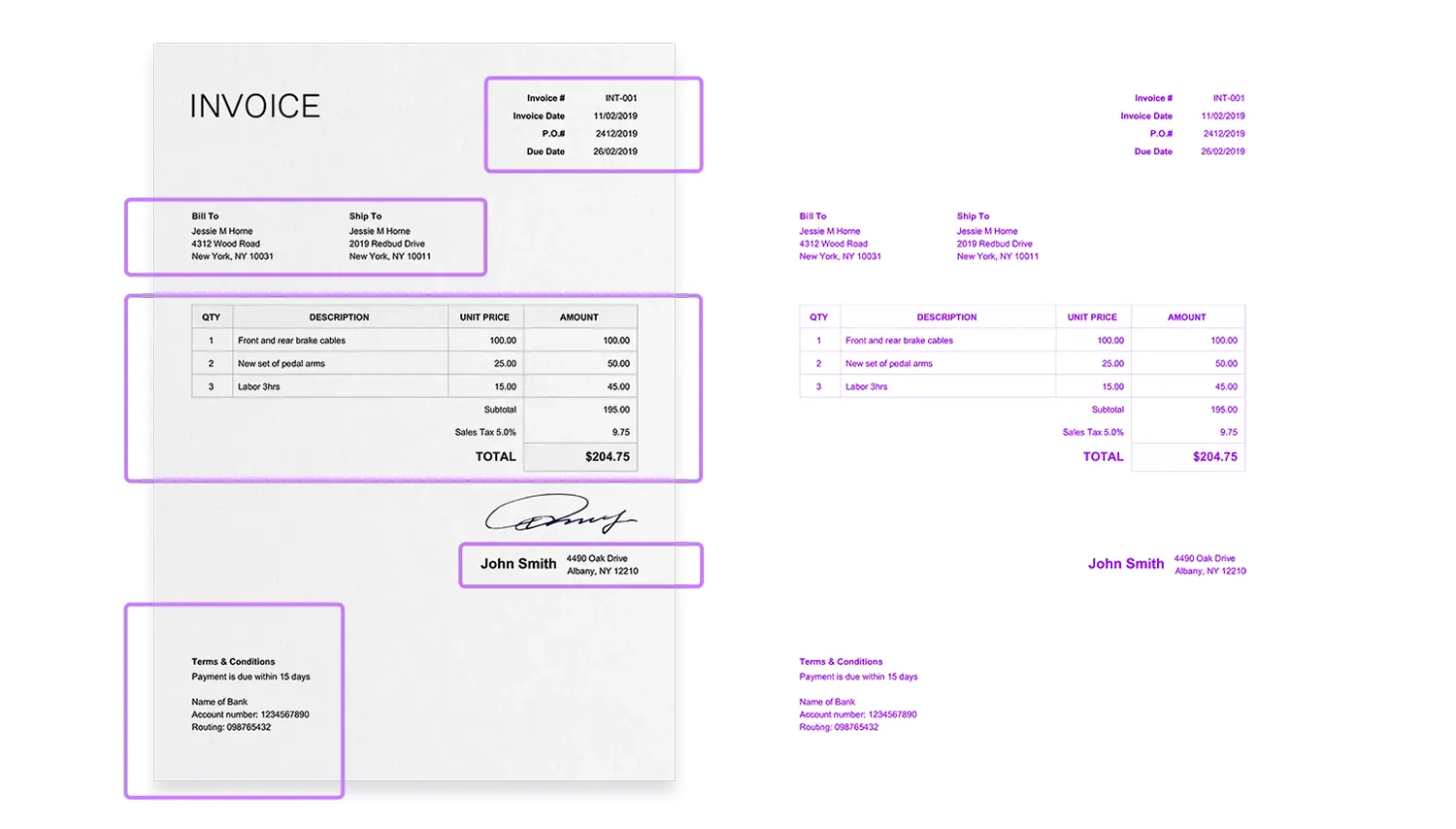
With OCR, all or specific textual data from a physical medium such as a bank statement can be recognized and converted into plain text, ready to be entered into a company’s database.
OCR can process any type of image, including text that is printed or digitally scanned. The process typically includes three phases: detection, recognition, and post-processing.
First, a special algorithm—a text detector—finds and pinpoints the text areas in the image. Then, the text is recognized using pattern recognition and/or machine learning algorithms. In practice, this means matching characters in the image with letters and numbers from the chosen language.
Finally, OCR prepares the recognized text for export and storage, validating and correcting it if needed. For instance, at this phase, mismatches such as confusing the letter “O” and the number “0” can be detected and corrected.
Subscribe to receive a bi-weekly blog digest from Regula
In remote identity verification, OCR plays an even more critical role. It not only converts imaged text into editable content but also replaces human inspectors by examining specific parts of physical documents presented by users far from a bank office.
Let’s look at common technology applications in banking.
What is OCR in banking: Main tasks
With the rise of neobanks—often operating without physical offices—and the digitalization of traditional financial institutions, there’s a growing demand for smart automation in banking workflows, including startup banking. OCR is essential for many of these routine operations.
Here are just a few OCR use cases in banking:
Customer onboarding
Signing up for a digital banking service may require document authentication as a mandatory step. The user must scan their government-issued ID to confirm their identity. Even if this check is partly manual—for instance, through a video chat with a bank representative—sending a scanned ID is a required prerequisite.
OCR handles this task effectively. It can also be used for auto-filling registration forms, which is another typical step for first-time bank customers. Critical details for banks, such as full name, date of birth, address, and document number, can be easily extracted from the ID and automatically entered into the bank’s system. This not only speeds up onboarding but also reduces human errors like incorrect data entry.
Opening a bank account remotely
Identity verification (IDV), when required, may also be applied later for registered users, and only for certain transactions like opening a bank account. In this case, OCR performs the same function: pulling personal details from documents to be checked manually or via an automated IDV solution.
Payment automation
OCR is helpful in payment services, particularly for bank card recognition. When users link their bank cards for online payments, for example, on ecommerce platforms, they don’t need to input their card data manually. Bank card recognition technology detects the cardholder’s name, number, and expiration date by using visual zone OCR to read both sides of the card.
This automation makes the transaction quick and accurate while improving the user experience.
Bank documentation OCR
The technology works not only in customer interactions but also in internal operations. Traditional banks still deal with a lot of paperwork, including printed official documents.
OCR helps by speeding up data capture from scanned or photographed checks, bank statements, loan applications, credit reports, tax returns, and other documents, turning them into machine-readable formats.
To enable this, template-based OCR is often used. This algorithm creates document maps for common formats. As a result, it can locate key elements and data fields, for example, the date in the upper-right corner of an invoice, or the total amount at the bottom.
AML and KYC compliance
It may not be obvious, but OCR also contributes significantly to security. All banking organizations must comply with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) rules and address threats like terrorism financing and identity fraud by implementing Know Your Customer (KYC) frameworks as part of their daily routine.
Accurate capture of financial and personal data from identity and official documents is key to these policies. OCR not only saves time and money on document processing and data entry but also prevents any critical errors and mismatches between document information and self-reported data.
Components of the right OCR engine for banking
On the one hand, OCR in banking may seem like a standard procedure, meaning any engine can perform this task equally well. However, there are always tiny details that might be overlooked, from poor image capture to outdated engines not trained for global ID formats.
Before we dive deeper, it’s important to note that when it comes to IDV, overreliance on OCR without additional checks like liveness detection or facial match is unacceptable for secured systems.
Now, what are the critical points to consider when implementing OCR technology in banking?
Data extraction accuracy
Not all OCRs are created equal. To extract data accurately, the solution must be regularly updated. This starts with ID recognition, since there are thousands of document types worldwide.
From the beginning, the IDV solution you use should include a document template database suited to your operational region. For instance, Regula has the world’s largest ID library with over 16,000 items from 254 countries and territories. This ensures support for a wide range of IDs—national ID cards, passports, driver’s licences, proof of residency (like visas or residence permits), and even rarer forms of IDs—issued in 138 languages.
Document templates should also be revisited regularly to ensure each field is accurately recognized based on current usage. For example, some IDs use right-to-left scripts like Hebrew or Arabic, or include diacritical marks like è, ē, and ë. These details must be considered to optimize recognition speed and ensure correct rendering of non-Latin characters.

IDs in Arabic, like the Algerian driver’s license, use right-to-left scripts and sometimes require longer data fields.
OCR for fields with noisy or colorful backgrounds can be a challenge. When the algorithm “knows” that a certain passport features a hologram that partially masks data fields, it can use experience from previous sessions with the same ID type to extract the information more accurately.

Intricate background patterns are common in domestic ID documents. For example, in the Monaco travel document issued to foreign residents, complex design can challenge OCR—especially for the Name and Sex fields.
Data processing speed
Although OCR is typically fast, processing can still be optimized. For example, before data extraction, the algorithm usually crops the document and identifies its type. In some cases, these pre-steps can be skipped to speed things up. Only selected tasks, such as data reading or autofill, will be executed. This is especially useful in document OCR for banking, where only specific operations, such as extracting a total transaction amount, are needed.
This requires proper settings in the OCR engine. Regula Document Reader SDK is a fully customizable tool that offers such flexibility.
It’s also essential to use modern OCR engines that support UTF-8 encoding, especially if you process documents with non-Latin scripts.
Older systems may be limited to 256 bytes per field, which works well for Latin scripts (where one character typically equals one byte). However, non-Latin scripts, like Arabic or Chinese, often require 2-4 bytes per character. This means longer data from fields like Name or Address might be truncated.
UTF-8 encoding, with no fixed byte limit, enables support for longer fields and multilingual scripts without data loss.

Multilingual fields are common in travel documents. For example, the Azerbaijan passport displays key details—like the holder’s name, nationality, place of birth, and sex—in both the country’s official language and English.
Support for recognizing text in security features
ID documents often contain text outside the visual inspection zone (VIZ), and OCR must handle this as well. There’s also a machine-readable zone (MRZ), which includes a unique font and various security features like watermarks, Multi Laser Images (MLIs), and perforated numbers with critical data.

MLIs—like the one in Arizona’s 2023 driver’s license—often include the holder’s date or year of birth. This data can also be extracted using OCR.
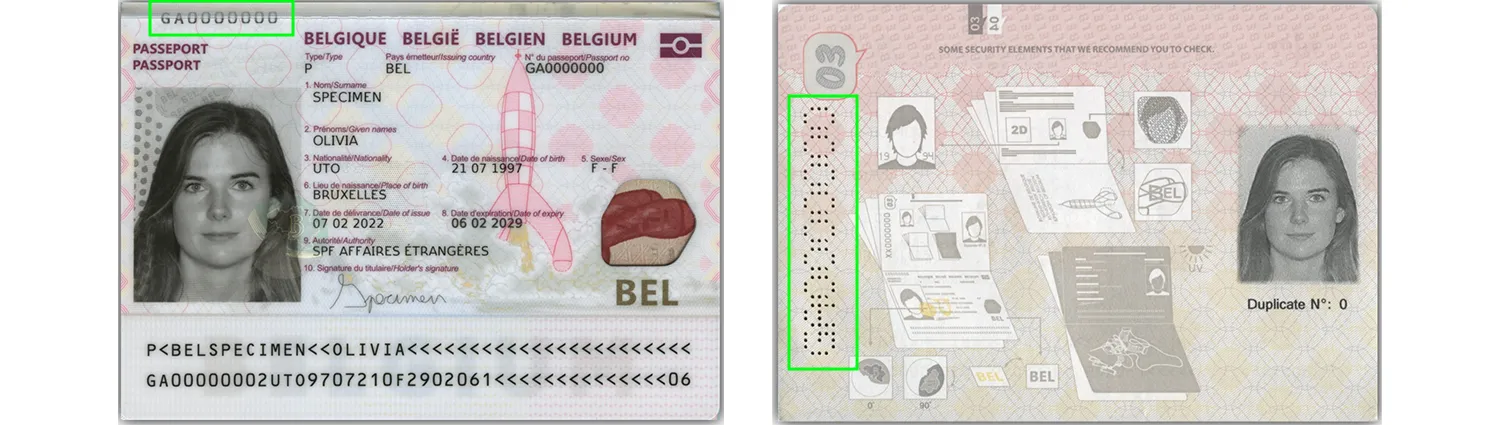
The ID number—found in the visual and machine-readable zones—can also appear as a perforated number on the inner pages and as a security feature at the data page junction, as shown in Belgium’s 2022 passport.
Advanced OCR can extract this information and prepare it for cross-checking, when data from different document sections is matched to spot inconsistencies.
Performance in low-quality scenarios
This is a common challenge: OCR requires high-quality images to work well. Your IDV solution should therefore include tools for document capture and preprocessing. For instance, Regula Document Reader SDK supports advanced capture and image quality assessment to ensure a good scan on the first try. This reduces the number of blurry, darkened, or cropped images users submit.
User experience
Finally, OCR must be intuitive for customers. From their side, it’s just about scanning an image. However, they still need clear instructions on how to do it properly, ideally in their native language. Banks that neglect this may face higher drop-off rates, which is critical in such a competitive market.
Regula’s SDK supports localization in 30+ languages and 100% interface customization, making it easy to integrate a smooth OCR experience into your bank’s app or web platform.
Key takeaways: Requirements for OCR technology in banking
Financial institutions must follow strict regulations, including KYC and AML rules for collecting, processing, and analyzing personal data. Failing to comply can lead to heavy fines and serious reputational damage. Advanced OCR adds accuracy to this process.
Banks are required to verify the identities of customers who may be located anywhere in the world. OCR plays a key role here. For remote verification, this demands a global document template database to accurately read and extract the necessary information.
Beyond ID documents, banks also handle official papers that contain critical data. Fast and reliable OCR helps automate data entry and reduces errors, saving staff time.
Accurate OCR starts with a quality image. A user-friendly interface improves customer experience and helps ensure that ID or bank card scans succeed on the first try.
Verify your customers securely with Regula
Regula OCR technology supports 138 languages, including non-Latin scripts, and performs lexical analysis to validate field context.
But OCR is just the first step in the IDV process. To confirm the identity of a remote customer a bank has never met in person, a full set of document and biometric checks is required. Regula offers advanced tools with liveness detection for both IDs and selfies, along with extra safeguards like server-side reverification for electronic IDs.
See what our banking clients say—and book a call to discuss your specific case.



.webp)

