Updated September 19, 2025
Think of the last time you opened a bank account. If it was fairly recently, the teller probably scanned your ID, and within seconds, your information was in their system. That’s where ID scanners come in. They use optical character recognition (OCR) software to quickly capture data from IDs, automating the entry process.
However, the term "ID scanner" covers a wide range of tools, from mobile apps to specialized forensic ID scanners.
In this article, we’ll have a look at the most common types of ID scanners and how they can benefit your organization.
Get posts like this in your inbox with the bi-weekly Regula Blog Digest!
Is it an ID scanner or a document reader?
ID scanners are often referred to as document readers or passport readers. In some contexts, the terms can be synonymous, but as a rule, readers have more powerful capabilities. Both scanners and readers leverage an OCR engine that is able to capture symbols and feed them into the system.
But, unlike ID scanners, passport readers also allow you to authenticate the data: identify the document type; make sure it’s valid; check the data encoded in machine-readable zones, barcodes, and chips; and even examine the security features of IDs under different light sources.
Depending on the context of use and how deeply the documents need to be checked, you can choose from stationary and embedded readers for onsite use, mobile document readers for field operations, or software development kits (SDKs) to integrate into apps. (Explore our guide on choosing the best document readers for your business.)
Let’s look at the typical use cases when ID scanners come in handy and which types of ID scanners can be used.
Use case #1: Border control and law enforcement identity checks
Use case #2: Data entry automation and ID verification for businesses
Use case #1: Border control and law enforcement identity checks
This use case likely involves the widest variety of types of ID scanners in use.
On-site document readers are vital in border control and law enforcement, speeding up the validation of passports, visas, ID cards, and more. These devices, equipped with advanced light sources and scanning features, help detect counterfeit documents.
Desktop document readers are the backbone of border control operations at immigration checkpoints, airports, and governmental agencies. Compact yet powerful, these devices are tailored specifically for fast and accurate passport processing. They are widely appreciated for their affordability, small footprint, and ability to perform sophisticated authenticity checks, such as reading embedded chips, optical variable inks, and holograms.
Device example: Regula 70X4M. Different modifications of this device are used, for example in Austria by the municipal registration offices and by the Aruban Immigration Authority.
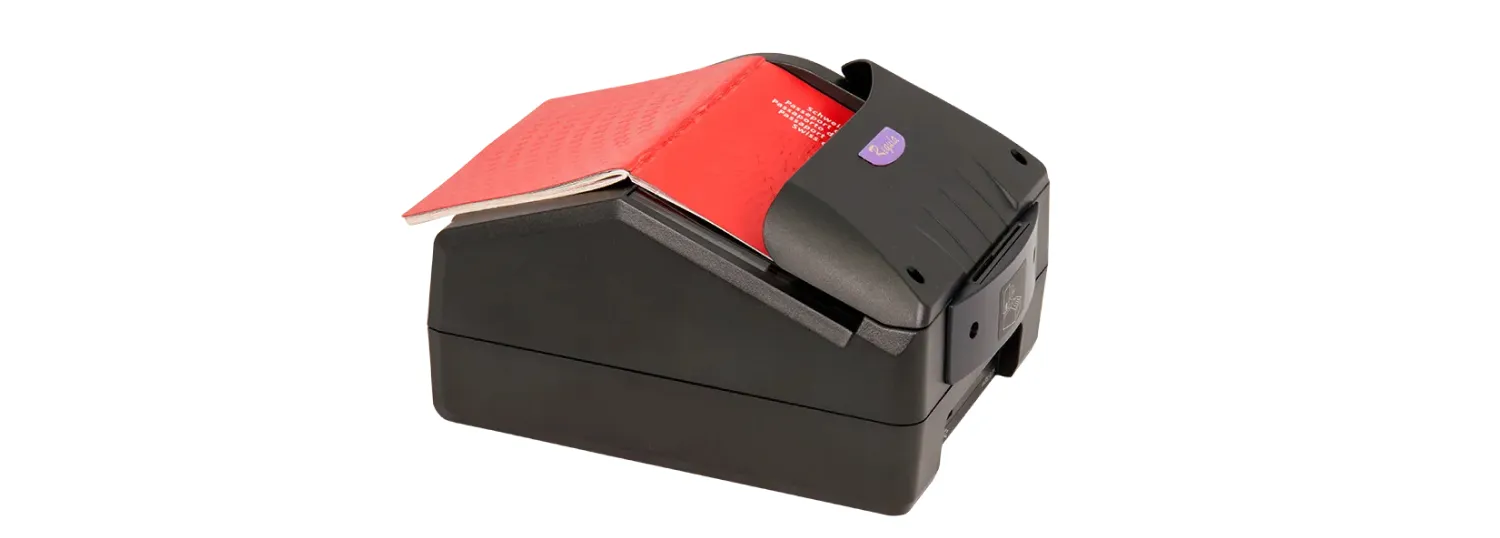

Standalone workstations take document verification to the next level by integrating a built-in computer, eliminating the need for an external PC to manage the data. These all-in-one devices are particularly useful in space-constrained environments like border control counters, police stations, and immigration offices. In addition to reading and verifying documents, standalone workstations can store and analyze data independently, making them an efficient solution for remote or decentralized locations where additional IT infrastructure is unavailable.
Device example: Regula 70X9.

Embedded document readers are the core technology behind automated border control kiosks, e-gates, and check-in counters. These readers are designed for self-service scenarios where travelers scan their own documents. Built to withstand heavy use, these devices offer advanced verification features to check security elements like UV printing, infrared patterns, and RFID chips. Their primary function is to allow fast, automated document processing while ensuring the highest level of security.
Device example: Regula 70X8M.

Embedded readers vary in the document formats they can verify. In addition to passports, ID1-format documents—primarily identity cards and driver’s licenses—are also widely used for travel. To handle these, Regula 7223E offers dual-side scanning, supports card insertion in any orientation, and automatically ejects cards after scanning.
These reader variations are sometimes installed in pairs at e-gates or kiosks. In fact, Regula embedded readers, which run on the same document verification software, support this configuration.
Device example: Regula 7223E
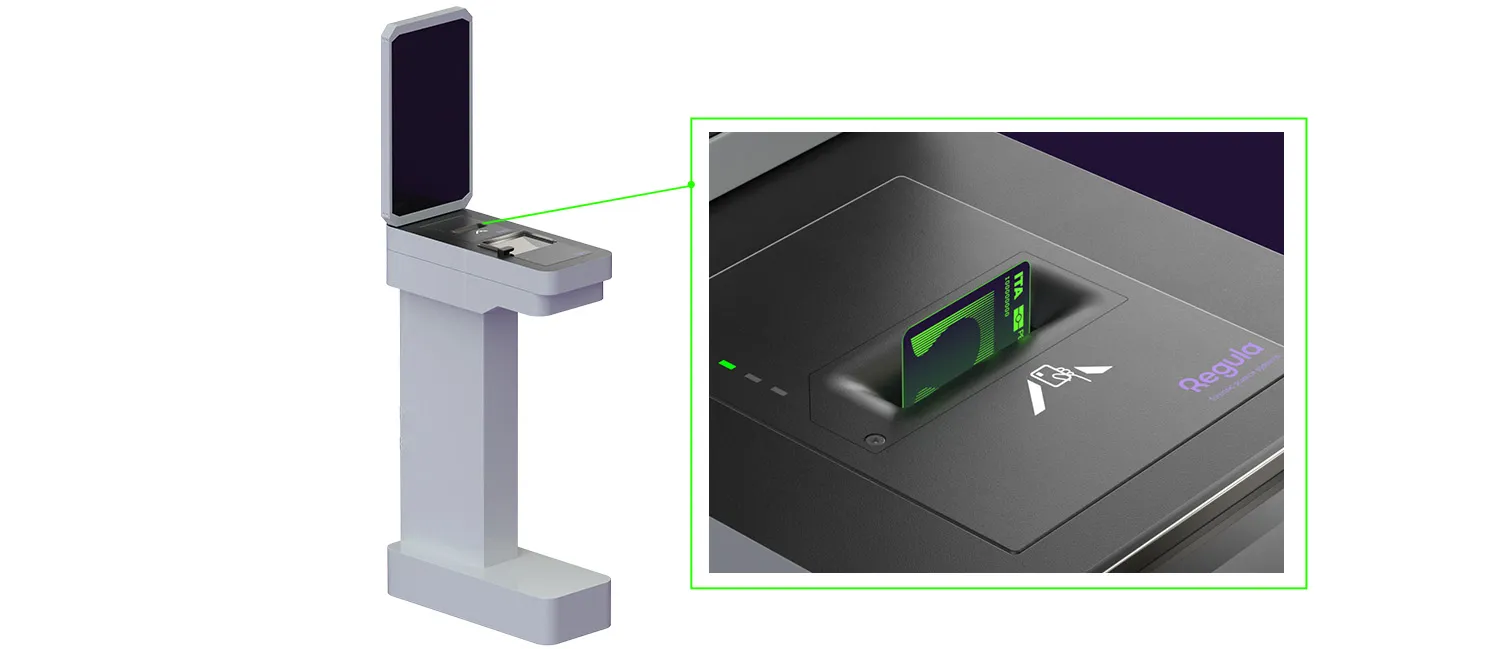
Field operations demand equipment that is not only portable but also durable and efficient. Border patrol agents and law enforcement officers need to perform on-the-spot identity checks, often in remote or high-mobility environments.
Portable workstations are designed specifically for agents on the move. These devices resemble desktop workstations but are built for fieldwork. Equipped with a rechargeable battery and multiple fastening options (such as shoulder or waist straps), they provide maximum mobility while still allowing for advanced document verification. Officers can wear them securely, leaving their hands free to handle other tasks or equipment.
Device example:Regula 7308.

Mobile document readers are handheld devices appreciated by road police, border patrols, and surveillance agencies. Some of these readers have a built-in computer that processes and analyzes the data on the spot, so they can work independently. This can be especially important in remote areas where internet connectivity is unreliable or unavailable. Others connect to a centralized system and can be used as a part of a larger ecosystem.
Device example:Regula 7310.

Use case #2: Data entry automation and ID verification for businesses
ID scanners are no longer limited to government use. In fact, businesses across various industries have adopted document readers for seamless data entry and verification. Banks, for example, use ID scanners extensively for quick and reliable document processing during customer onboarding. These scanners allow them to verify the validity and authenticity of IDs, helping to mitigate fraud and speed up client verification processes.
In sectors like hospitality, healthcare, casinos, or even nightclubs, desktop document readers offer fast and simple ID checks. Here, speed and efficiency are prioritized over advanced authenticity checks, as the main goal is to capture basic data for entry into customer management systems or to comply with age verification laws.
Device example: Regula 70X7.

In addition to verification scenarios that allow any ID type, some use cases require presenting specific identity documents, such as driver’s licenses, ID cards, and other ID-1 format documents. These situations necessitate duplex hardware solutions capable of simultaneously reading and verifying both the front and reverse sides of the ID document.
Device example: Regula 72X3 is specifically designed for ID-1 authentication. Some configurations include additional modules to read RFID chips, smart cards, and magnetic stripes, expanding its functionality. For instance, it can verify biometric ID cards and bank cards.

In addition to hardware devices, many businesses are turning to software-based ID verification solutions. If you’ve ever used mobile banking, or, for example, enrolled in a crypto trading exchange, then you know the drill: before accessing services, you need to prove your identity by scanning your ID, taking a selfie, scanning your bank card, and sometimes passing a liveness check to make sure it’s really you.
These capabilities can be provided by software development kits (SDKs) that integrate directly into the company’s systems. The primary function of these solutions is to ensure reliable and secure customer onboarding. By automating the process, businesses can reduce the manual labor involved in data entry while maintaining a high level of security and compliance.

When SDKs meet document readers
ID document readers, while 100% hardware-based, rely on software for precise automated authenticity verification. Software also performs basic tasks like data capture, recognition, and automating data entry, as well as more advanced functions such as RFID chip verification. In practice, these components often collaborate seamlessly. For example, Regula Document Reader SDK is compatible not only with the company’s own readers but also with third-party devices.
How companies use ID scanners
Even within one organization, document readers can find applications for multiple use cases.
Customer onboarding
In most cases, onboarding is a simple process, but for highly-regulated industries like Banking, it’s more complex. Banks and financial institutions must collect personal information right from the start, which can lead to higher abandonment rates if the process is too slow or tedious.
By using professional ID scanners, organizations can extract personal data and verify identity in seconds—the process is often as easy as taking a selfie. Pearson VUE, a leader in online testing, uses this technology for remote authentication via selfies and passport verification. Such methods of bringing in new customers are applicable in many industries worldwide.
KYC automation
Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures are mandatory in many industries to prevent fraud. ID scanners simplify KYC by providing fast, accurate passport verification. Automating these processes with scanners not only speeds up the workflow but also reduces errors, creating a smoother experience for customers.
Check-in automation
Self-service, contactless check-ins are becoming the new standard, particularly after the pandemic. Traditional check-ins are often slow, but ID scanners can extract data and verify documents much faster. Airlines, hotels, and many other businesses now use automated check-in systems to speed up the process.
For example, Pegasus Airlines has transformed its check-in process. Passengers can now scan their ID through the app, select a flight, and complete the check-in in seconds.
Age verification
For industries that must restrict underaged access—like casinos, alcohol retailers, or adult-only events—automated age verification is crucial. ID scanners, equipped with OCR technology, can instantly verify age and flag any fake or borrowed IDs.
Adding a solution like Regula Face SDK provides an extra layer of security by comparing the selfie with the ID photo to ensure the person presenting the ID is its rightful owner.
Restricted access management
High-security facilities, such as government buildings, courts, embassies, and prisons, must verify every visitor. They may also need to keep the ID data to comply with security regulations. A visitor management system that is based on automated ID scanning and verification is easy to deploy and maintain, and it doesn’t leave room for human error.
How ID scanners work and what they can detect
The heart of any ID scanner or reader is basically a camera. The device takes photos of identity documents and then examines them. The main difference between examination with hardware and software-based mobile document readers is the shooting conditions.
Software solutions exploit the capabilities of the user’s device. They also rely on the user’s accuracy at taking photos, which is why they may quite often ask users to retake an image of a document if the previous result had glares or was blurry.
Desktop and embedded passport readers allow you to examine documents in various light sources, such as white, infrared, ultraviolet, and coaxial. Importantly, they also provide perfect shooting conditions. There is no ambient light or glare, so you can, for example, capture UV luminescence without the intrusion of ambient light. Plus, there’s no need to hold documents with your hands, so they will be perfectly flat and no parts will be covered with fingers. This gives passport readers the upper hand in document authentication.
From a bird’s eye view, using an ID scanner—primarily, the software it relies on—involves the following steps:

1. Capture
Capturing a document image is an important step. A low-quality image or a photo taken at an angle or with poor lighting can make it difficult to read the information on the document, leading to errors. It can also make it harder to spot any signs of forgery, such as alterations of the text. In many cases, it’s also important to save the images for further audit.
ID scanners easily handle this task. While hardware document readers excel at scanning and capturing images by default, software solutions often rely on advanced algorithms to get the best shot on the first try. At this stage, RFID chips in biometric documents are also read.
2. Recognition
Then, the solution recognizes text symbols within images (e.g., passport scans), translates them into data, and sends that data into one or more systems for further use. This function is used, for example, in hotels. Equipped with a passport reader, a receptionist doesn’t have to enter the guests’ personal data manually, which greatly accelerates the check-in process and improves the customer experience.
3. Verification
Verification ensures that the ID is authentic and valid. Depending on the device or software, checks can include comparing the document’s expiration date, or even using biometric verification.
For example, Regula Document Reader SDK matches the data in the visual inspection zone with machine-readable zones and barcodes. Paired with Regula Face SDK, it can also verify the document holder’s portrait against the images stored on the chip.
It’s also important to keep in mind that in order to be able to reliably verify a document, a vendor needs to have an extensive library of document templates to compare the provided documents against references. Otherwise, the ID scanner is only suitable for very basic document verification.
What else can a professional ID scanner detect?
Professional document readers should be able to extract and verify the following data:
- Document type;
- All textual and numeric fields, be they typed, printed, or embossed (e.g., name or date of birth);
- Information from machine-readable zones (MRZs);
- Information from barcodes and QR codes;
- Information from electronic chips.
Plus, they perform extended authenticity checks based on images taken in different light sources.
To sum up: Why using ID scanners is worth a shot
Automated document reading has a simple and clear value: it quickly retrieves personal details and verifies them in seconds. As you can see, there are many types of ID scanners, but all of them have a number of benefits in common:
Faster processing: ID scanners process documents in just a second or two, compared with manual data entry, which is slower and more prone to error—especially with complex foreign names or similar-sounding ones (e.g., Kira and Kyra).
Reduced errors: Technology outperforms humans in repetitive tasks, eliminating misprints and keeping data consistent across systems.
Less workload for staff: High traffic can overwhelm personnel, leading to mistakes and higher probability of overlooking suspicious/fake IDs. ID scanners minimize this burden, allowing staff to focus on more critical tasks.
Enhanced security: Document readers go beyond basic OCR by cross-checking extracted data with various security features. This effectively safeguards the organization without requiring extra effort or extensive training.
Easier compliance: Proper document readers can read and verify any ID document from any country, streamlining the onboarding process and conducting it in accordance with local regulations.
These are only a few examples of how automated ID data extraction and verification can help your business become more effective and successful. If you’d like to learn more about what type of ID scanner can better serve your goals, or how to build an effective verification pipeline, feel free to consult with the experts from Regula.



.webp)

